1、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 void get_n(char * ar, int n); int main(void) { int n; printf("n = "); scanf("%d", &n); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; char st1[SIZE]; get_n(st1, n); puts(st1); int i; for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("st1[%d]: %c\n", i, st1[i]); } return 0; } void get_n(char * ar, int n) { int i; puts("please input the elements of the strings."); for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%c", &ar[i]); } }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 40 char * read_char(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char test[SIZE]; puts("Start to test function, enter a string."); read_char(test, 5); puts("The string you input is: "); puts(test); return 0; } char * read_char(char *st, int n) { int i = 0; do { st[i] = getchar(); } while(st[i] != EOF && ++i < n); return 0; }
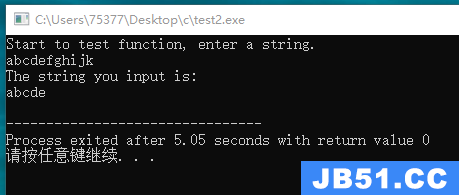
2、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 40 char * read_char(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char test[SIZE]; puts("Start to test function, enter a string."); read_char(test, 5); puts("The string you input is:"); puts(test); return 0; } char * read_char(char *st, int n) { int i = 0; do { st[i] = getchar(); if(st[i] == '\n' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == ' ') break; } while(st[i] != EOF && ++i < n); return st; }

3、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * get_word(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char word[SIZE]; char * temp; temp = get_word(word, SIZE); puts(temp); return 0; } char * get_word(char *st, int n) { char * temp; int i = 0; temp = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(temp) { if(st[0] == ' ') { while(st[i] == ' ') i++; } } temp += i; while(st[i] != ' ' && st[i] != '\t' && st[i] != '\n') i++; st[i] = '\0'; return temp; }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * get_word(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char word[SIZE]; char * temp; temp = get_word(word, SIZE); puts(temp); return 0; } char * get_word(char *st, int n) { char * temp; int i = 0; temp = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(temp) { if(st[0] == ' ') { while(st[i] == ' ') i++; } } temp += i; while(st[i] != ' ' && st[i] != '\t' && st[i] != '\n') i++; if(st[i] == ' ' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; return temp; }
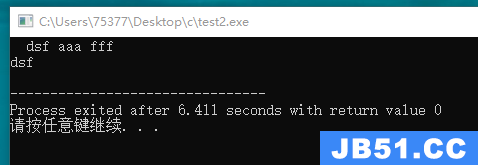
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #define SIZE 80 char * get_word(char *out); int main(void) { char output[SIZE]; get_word(output); printf("the first word you input is: %s", output); return 0; } char * get_word(char *out) { char input[SIZE]; char *in = input; puts("enter a string: "); fgets(input, SIZE, stdin); while((*in == '\n' || *in == '\t' || *in == ' ') && *in != '\0') in++; while(*in != '\n' && *in != '\t' && *in != ' ' && *in != '\0') *out++ = *in++; return out; }
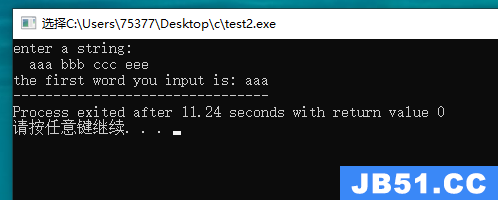
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * get_word(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char word[SIZE]; char *tmp; tmp = get_word(word, SIZE); puts(tmp); return 0; } char * get_word(char *st, int n) { char *tmp; int i = 0; tmp = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(tmp) { while((st[i] == ' ' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == '\n') && st[i] != '\0') i++; tmp += i; while(st[i] != ' ' && st[i] != '\t' && st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0' ) i++; if(st[i] == ' ' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return tmp; }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * get_word(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char * fword; printf("please input the strings.\n"); fword = get_word(st1, SIZE); printf("first word: %s\n", fword); return 0; } char * get_word(char *st, int n) { char * temp; int i = 0; temp = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(temp) { while((st[i] == ' ' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == '\n') && st[i] != '\0') i++; temp += i; while(st[i] != ' ' && st[i] != '\t' && st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == ' ' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return temp; }
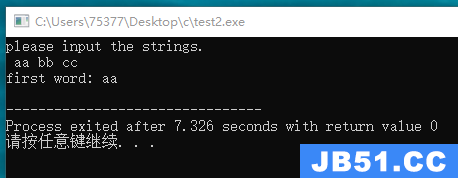
4、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * get_word(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char * fword; printf("please input the strings.\n"); fword = get_word(st1, SIZE); printf("first word: %s\n", fword); return 0; } char * get_word(char *st, int n) { char * temp; int i = 0; temp = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(temp) { while((st[i] == ' ' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == '\n') && st[i] != '\0') i++; temp += i; while(st[i] != ' ' && st[i] != '\t' && st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == ' ' || st[i] == '\t' || st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return temp; }

5、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * search_ch(char * ar, char ch); char * s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char * find; char ch; char xx; do { puts("input the string: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); printf("please input the ch: "); scanf("%c", &ch); find = search_ch(st1, ch); if(find) puts(find); else puts("nothing found!"); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; printf("quit(q to quit!); other continue xx: "); scanf("%c", &xx); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } while(xx != 'q'); return 0; } char * search_ch(char * ar, char ch) { int i = 0; char * find; while(ar[i] != ch && ar[i] != '\0') i++; if(ar[i] == ch) find = ar + i; else find = NULL; return find; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

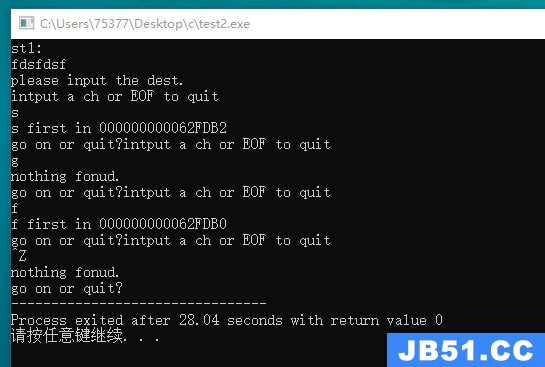
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 81 char * get_pos(char *st, char ch); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("st1: \n"); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); char des = ' '; char *pos; printf("please input the dest.\n"); while(des != EOF) { printf("intput a ch or EOF to quit\n"); while((des = getchar()) == '\n') continue; if((pos = get_pos(st1, des)) != NULL) printf("%c first in %p\n", *pos, pos); else printf("nothing fonud.\n"); printf("go on or quit?"); } return 0; } char * get_pos(char *st, char ch) { while(*st != '\0') { if(*st == ch) return st; else st++; } return NULL; }
6、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 int find_ch(char ch, char * ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char target; printf("please iput the strings: "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); while(1) { printf("please input target character(EOF to quit): "); target = getchar(); if(target == EOF) break; while(getchar() != '\n') continue; if(find_ch(target, st1) != 0) { printf("find the target!\n\n"); } else { printf("not fond the target!\n\n"); } puts("go on or quit? "); } } int find_ch(char ch, char * ar) { while(*ar != '\0') { if(*ar == ch) return 1; else ar++; } return 0; }

6、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * s_gets(char *st, int n); int find(char ch, char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; puts("please input the strings."); s_gets(st1, SIZE); char target; while(1) { printf("please input the target character(EOF to quit).\n"); target = getchar(); if(target == EOF) break; while(getchar() != '\n') continue; if(find(target, st1) != 0) { puts("find the target!\n"); } else { puts("not find the target!\n"); } puts("go on or quit? "); } } int find(char ch, char *ar) { while(*ar) { if(*ar == ch) return 1; else ar++; } return 0; } char * s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

7、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 80 char * mystrncpy(char * ar1, char * ar2, int n); char *s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char st2[SIZE]; printf("input source string: "); s_gets(st2, SIZE); int num; printf("input copy number: "); scanf("%d", &num); mystrncpy(st1, st2, num); printf("string copy result: %s\n", st1); return 0; } char * mystrncpy(char * ar1, char * ar2, int n) { int i = 0; while(i < n && ar2[i] != '\0') { ar1[i] = ar2[i]; i++; } if(i < n) { while(i < n) { ar1[i] = '\0'; i++; } } return ar1; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

循环:
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 80 char * mystrncpy(char * ar1, char * ar2, int n); char *s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char st2[SIZE]; while(1) { printf("input source string(q to quit): "); s_gets(st2, SIZE); if(strcmp(st2, "q") == 0) break; int num; printf("input copy number: "); scanf("%d", &num); mystrncpy(st1, st2, num); printf("string copy result: %s\n", st1); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return 0; } char * mystrncpy(char * ar1, char * ar2, int n) { int i = 0; while(i < n && ar2[i] != '\0') { ar1[i] = ar2[i]; i++; } if(i < n) { while(i < n) { ar1[i] = '\0'; i++; } } return ar1; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 80 char * mystrncpy(char * ar1, char * ar2, int n); char *s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char st2[SIZE]; char ch; while(1) { printf("input source string(EOF to quit): "); if((ch = getchar()) == EOF) break; s_gets(st2, SIZE); int num; printf("input copy number: "); scanf("%d", &num); mystrncpy(st1, st2, num); printf("string copy result: %s\n", st1); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return 0; } char * mystrncpy(char * ar1, char * ar2, int n) { int i = 0; while(i < n && ar2[i] != '\0') { ar1[i] = ar2[i]; i++; } if(i < n) { while(i < n) { ar1[i] = '\0'; i++; } } return ar1; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

8、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 80 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char st2[SIZE]; printf("st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); printf("st2: "); s_gets(st2, SIZE); char * scan_re; scan_re = scan(st1, st2); if(scan_re) { puts("\noverlapping!"); puts(scan_re); } else puts("\nnot overlapping!"); return 0; } char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2) { int i = 0; while(ar1[i] != '\0') { if(ar1[i] == ar2[0]) { int j = 0; while(ar1[i + j] == ar2[j] && ar2[j] != '\0') j++; if(ar2[j] == '\0') return ar1; } i++; } return NULL; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * s_gets(char *st, int n); char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char st2[SIZE]; char * scan_re; printf("please input st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); printf("please input st2: "); s_gets(st2, SIZE); scan_re = scan(st1, st2); if(scan_re) { puts("overlapping!"); puts(scan_re); } else { puts("not overlapping!"); } return 0; } char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2) { int i = 0; while(ar1[i] != '\0') { if(ar1[i] == ar2[0]) { int j = 0; while(ar1[i + j] == ar2[j] && ar2[j] != '\0') j++; if(ar2[j] == '\0') return ar1 + i; } i++; } return NULL; } char * s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }
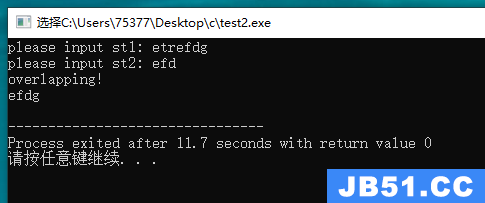
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char * s_gets(char *st, int n); char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; char st2[SIZE]; char * scan_re; char temp; while(1) { printf("please input st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); printf("please input st2: "); s_gets(st2, SIZE); scan_re = scan(st1, st2); if(scan_re) { puts("overlapping!\n"); puts(scan_re); } else { puts("not overlapping!\n"); } printf("y continue or EOF to quit): "); if((temp = getchar()) == EOF) break; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return 0; } char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2) { int i = 0; while(ar1[i] != '\0') { if(ar1[i] == ar2[0]) { int j = 0; while(ar1[i + j] == ar2[j] && ar2[j] != '\0') j++; if(ar2[j] == '\0') return ar1 + i; } i++; } return NULL; } char * s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 char * scan(char *ar1, char *ar2); char * s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char ar1[SIZE]; char ar2[SIZE]; char * result; printf("ar1: "); s_gets(ar1, SIZE); printf("ar2: "); s_gets(ar2, SIZE); while(*ar1 != '\n') { result = scan(ar1, ar2); if(result) { puts("overlapping!"); printf("result: %p\n", result); printf("result: %s\n", result); } else { puts("not overlapping!"); } printf("ar1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(ar1, SIZE); if(ar1[0] == '\0') break; printf("ar2: "); s_gets(ar2, SIZE); } return 0; } char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2) { int count = 0; int ar2_len = strlen(ar2); while(*ar1 != '\0' && count < ar2_len) { if(*(ar1 + count) == *(ar2 + count)) { count++; } else { count = 0; ar1++; } } if(count == ar2_len) { return ar1; } else return NULL; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 char * scan(char *ar1, char *ar2); char * s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char ar1[SIZE]; char ar2[SIZE]; char * result; printf("ar1: "); s_gets(ar1, SIZE); printf("ar2: "); s_gets(ar2, SIZE); while(*ar1 != '\0') { result = scan(ar1, ar2); if(result) { puts("overlapping!"); printf("result: %p\n", result); printf("result: %s\n", result); } else { puts("not overlapping!"); } printf("ar1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(ar1, SIZE); if(ar1[0] == '\0') break; printf("ar2: "); s_gets(ar2, SIZE); } return 0; } char *scan(char *ar1, char *ar2) { int count = 0; int ar2_len = strlen(ar2); while(*ar1 != '\0' && count < ar2_len) { if(*(ar1 + count) == *(ar2 + count)) { count++; } else { count = 0; ar1++; } } if(count == ar2_len) { return ar1; } else return NULL; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

9、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); void reverse(char *ar1); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); printf("origin st1: %s\n", st1); reverse(st1); printf("reverse st1: %s\n", st1); return 0; } void reverse(char *ar1) { int len = 0; while(*(ar1 + len)) { len++; } int i; char temp; for(i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) { temp = ar1[i]; ar1[i] = ar1[len - 1 - i]; ar1[len - 1 - i] = temp; } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

循环
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); void reverse(char *ar1); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; while(1) { printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); if(st1[0] == '\0') break; printf("origin st1: %s\n", st1); reverse(st1); printf("reverse st1: %s\n", st1); } return 0; } void reverse(char *ar1) { int len = 0; while(*(ar1 + len)) { len++; } int i; char temp; for(i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) { temp = ar1[i]; ar1[i] = ar1[len - 1 - i]; ar1[len - 1 - i] = temp; } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }
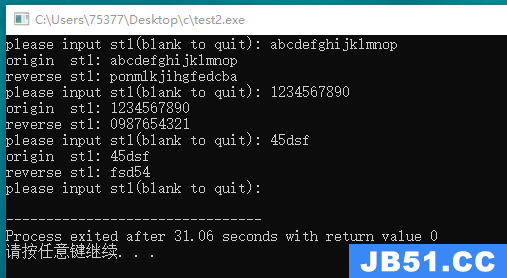
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); void reverse(char *ar1); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; while(*st1 != '\n') { printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); if(st1[0] == '\0') break; printf("origin st1: %s\n", st1); reverse(st1); printf("reverse st1: %s\n", st1); } return 0; } void reverse(char *ar1) { int len = 0; while(*(ar1 + len)) { len++; } int i; char temp; for(i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) { temp = ar1[i]; ar1[i] = ar1[len - 1 - i]; ar1[len - 1 - i] = temp; } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 char * invert(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); while(*st1 != '\n') { printf("origin st1: %s", st1); invert(st1); printf("invert st1: %s\n", st1); printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); } return 0; } char *invert(char *ar) { int len = strlen(ar); char temp[len]; int i; for(i = 0; i < len; i++) { *(temp + i) = *(ar + len - 1 - i); } for(i = 0; i < len; i++) { *(ar + i) = *(temp + i); } return ar; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 char *invert(char *ar); char *s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); while(*st1 != '\0') { printf("origin st1: "); puts(st1); invert(st1); printf("invert st1: "); puts(st1); printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); } return 0; } char *invert(char *ar) { int len = strlen(ar); char temp[len]; int i; for(i = 0; i < len; i++) { *(temp + i) = *(ar + len - 1 - i); } for(i = 0; i < len; i++) { *(ar + i) = *(temp + i); } return ar; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

10、
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); void del_space(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); printf("origin st1: "); puts(st1); del_space(st1); printf("delete st1: "); puts(st1); return 0; } void del_space(char *ar) { int i = 0; while(ar[i]) { if(ar[i] == ' ') { int j = i; while(ar[i]) { ar[i] = ar[i+1]; i++; } i = j; } else { i++; } } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); void del_space(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); while(*st1 != '\0') { printf("origin st1: "); puts(st1); del_space(st1); printf("delete st1: "); puts(st1); printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); } return 0; } void del_space(char *ar) { int i = 0; while(ar[i]) { if(ar[i] == ' ') { int j = i; while(ar[i]) { ar[i] = ar[i+1]; i++; } i = j; } else { i++; } } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); void del_space(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); while(1) { printf("origin st1: "); puts(st1); del_space(st1); printf("delete st1: "); puts(st1); printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); if(st1[0] == '\0') break; } return 0; } void del_space(char *ar) { int i = 0; while(ar[i]) { if(ar[i] == ' ') { int j = i; while(ar[i]) { ar[i] = ar[i+1]; i++; } i = j; } else { i++; } } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 void trim_space(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); while(*st1 != '\n') { printf("origin st1: %s", st1); trim_space(st1); printf("trim_space st1: %s", st1); printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); } return 0; } void trim_space(char *ar) { char *temp; temp = ar; int count = 0; while(*ar) { if(*ar != ' ') { *temp++ = *ar++; } else { ar++; count++; } } while(count--) *temp++ = '\0'; }
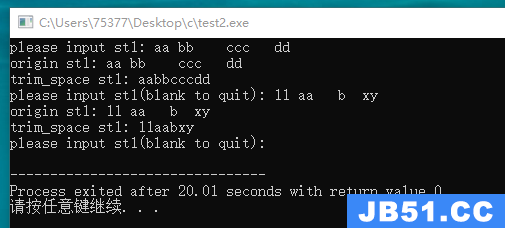
#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 void trim_space(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); while(*st1 != '\n') { printf("origin st1: %s", st1); trim_space(st1); printf("trim_space st1: %s", st1); printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); } return 0; } void trim_space(char *ar) { int i = 0; while(ar[i] != '\0') { if(ar[i] != ' ') { i++; } else { int j = i; while(ar[i] != '\0') { ar[i] = ar[i + 1]; i++; } i = j; } } }

#include <stdio.h> #define SIZE 100 void trim_space(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); while(*st1 != '\n') { printf("origin st1: %s", st1); trim_space(st1); printf("trim_space st1: %s", st1); printf("please input st1(blank to quit): "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); } return 0; } void trim_space(char *ar) { char *temp = ar; int count = 0; while(*ar != '\0') { if(*ar != ' ') { *temp++ = *ar++; } else { ar++; count++; } } while(count--) *temp++ = '\0'; }

11、
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdbool.h> #define SIZE 100 #define LIM 10 char *s_gets(char *st, int n); char menu(void); void print_origin(char ar[][100], int n); void print_sort(char *ar[], int n); void print_len(char *ar[], int n); void print_first(char *ar[], int n); int length(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[LIM][SIZE]; char *pt1[LIM]; int ct = 0; printf("please input the strings, EOF to quit.\n"); while(ct < LIM && s_gets(st1[ct], SIZE) != NULL && st1[ct][0] != EOF) { pt1[ct] = st1[ct]; ct++; } printf("please choose: \n"); char ch = menu(); while(ch != 'q') { switch (ch) { case 'a': print_origin(st1, ct); break; case 'b': print_sort(pt1, ct); break; case 'c': print_len(pt1, ct); break; case 'd': print_first(pt1, ct); break; case 'q': break; default: printf("a-d or q pleawe"); } ch = menu(); } return 0; } char menu(void) { printf("please input your choice!\n"); printf("a) print origin b) print sort by ASCII\n"); printf("c) print by length d) print by first word length\n"); printf("q) quit\n"); char ch = getchar(); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; return ch; } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char * ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; } void print_origin(char ar[][100], int n) { int i; puts("show the origin: "); for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { puts(ar[i]); } putchar('\n'); } void print_sort(char *ar[], int n) { char *temp; int i, j; for(i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for(j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if(strcmp(ar[i], ar[j]) > 0) { temp = ar[i]; ar[i] = ar[j]; ar[j] = temp; } } } puts("\nHere is the sorted by ASCII:"); for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { puts(ar[i]); } putchar('\n'); } void print_len(char *ar[], int n) { char *temp; int i, j; for(i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for(j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if(strlen(ar[i]) > strlen(ar[j])) { temp = ar[i]; ar[i] = ar[j]; ar[j] = temp; } } } puts("\nHere is show by length: "); for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { puts(ar[i]); } putchar('\n'); } void print_first(char *ar[], int n) { char *temp; int i, j; for(i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for(j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if(length(ar[i]) > length(ar[j])) { temp = ar[i]; ar[i] = ar[j]; ar[j] = temp; } } } puts("show the result sort by first word."); for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { puts(ar[i]); } putchar('\n'); } int length(char *ar) { int i = 0; int j = 0; bool inword = false; while(ar[i] != '\0') { if(inword == false && ar[i] != ' ') inword = true; if(inword == true && ar[i] != ' ') j++; if(inword == true && ar[i] == ' ') break; i++; } if(j != 0) return j; else return i; }

12、
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <stdbool.h> void basic(void); int main(void) { printf("please input strings(EOF to quit): \n"); basic(); return 0; } void basic(void) { char ch; int words = 0; int upper = 0; int lower = 0; int punct = 0; int digit = 0; bool inword = false; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(!isspace(ch) && inword == false) { words++; inword = true; } if(isspace(ch) && inword == true) { inword = false; } if(isupper(ch)) { upper++; } if(islower(ch)) { lower++; } if(ispunct(ch)) { punct++; } if(isdigit(ch)) { digit++; } } printf("words: %d\n", words); printf("upper: %d\n", upper); printf("lower: %d\n", lower); printf("punct: %d\n", punct); printf("digit: %d\n", digit); }

循环
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <stdbool.h> void basic(void); int main(void) { char ch; while(1) { printf("please input strings(EOF to quit): \n"); basic(); printf("blank to quit, other to contine: "); ch = getchar(); if(ch == '\n') break; while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return 0; } void basic(void) { char ch; int words = 0; int upper = 0; int lower = 0; int punct = 0; int digit = 0; bool inword = false; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(!isspace(ch) && inword == false) { words++; inword = true; } if(isspace(ch) && inword == true) { inword = false; } if(isupper(ch)) { upper++; } if(islower(ch)) { lower++; } if(ispunct(ch)) { punct++; } if(isdigit(ch)) { digit++; } } printf("words: %d\n", words); printf("upper: %d\n", upper); printf("lower: %d\n", lower); printf("punct: %d\n", punct); printf("digit: %d\n", digit); }

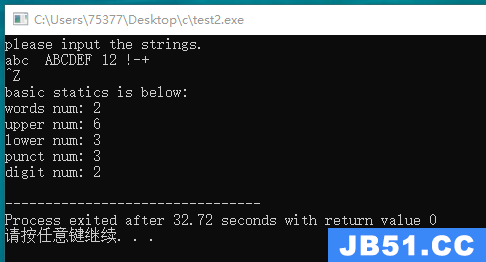
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #define SIZE 256 int check_words(char *input); int check_upper(char *input); int check_lower(char *input); int check_punct(char *input); int check_digit(char *input); int main(void) { char input[SIZE]; int i = 0; while((input[i++] = getchar()) != EOF) { if(i > SIZE) { printf("over flowed\n"); break; } } printf("basic static is below: \n"); printf("input words: %d\n", check_words(input)); printf("upper num: %d\n", check_upper(input)); printf("lower num: %d\n", check_lower(input)); printf("punct num: %d\n", check_punct(input)); printf("digit num: %d\n", check_digit(input)); return 0; } int check_words(char *input) { int count = 0; int start = 0; while(*input != EOF) { if(isalpha(*input) == 0 && start == 0) { input++; } else if(isalpha(*input) == 0 && start == 1) { count++; input++; start = 0; } else if(isalpha(*input) != 0) { start = 1; input++; } } if(start == 1) count++; return count; } int check_upper(char *input) { int count = 0; while(*input != EOF) { if(isupper(*input++) != 0) { count++; } } return count; } int check_lower(char *input) { int count = 0; while(*input != EOF) { if(islower(*input++) != 0) { count++; } } return count; } int check_punct(char *input) { int count = 0; while(*input != EOF) { if(ispunct(*input++) != 0) count++; } return count; } int check_digit(char *input) { int count = 0; while(*input != EOF) { if(isdigit(*input++) != 0) count++; } return count; }
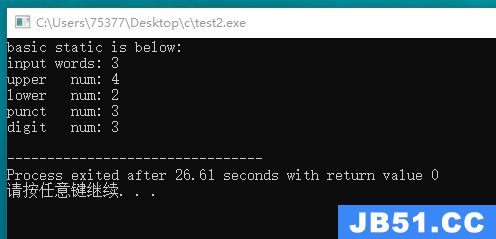
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #define SIZE 500 int words_check(char *ar); int upper_check(char *ar); int lower_check(char *ar); int punct_check(char *ar); int digit_check(char *ar); int main(void) { char input[SIZE]; int i = 0; puts("please input the strings."); while((input[i++] = getchar()) != EOF) { if(i > SIZE) { puts("number overflow!"); break; } } puts("basic statics is below: "); printf("words num: %d\n", words_check(input)); printf("upper num: %d\n", upper_check(input)); printf("lower num: %d\n", lower_check(input)); printf("punct num: %d\n", punct_check(input)); printf("digit num: %d\n", digit_check(input)); return 0; } int words_check(char *ar) { int count = 0; int start = 0; while(*ar != EOF) { if(isalpha(*ar) == 0 && start == 0) { ar++; } if(isalpha(*ar) == 0 && start == 1) { count++; ar++; start = 0; } if(isalpha(*ar) != 0) { ar++; start = 1; } } if(start == 1) count++; return count; } int upper_check(char *ar) { int count = 0; while(*ar != EOF) { if(isupper(*ar++) != 0) count++; } return count; } int lower_check(char *ar) { int count = 0; while(*ar != EOF) { if(islower(*ar++) != 0) { count++; } } return count; } int punct_check(char *ar) { int count = 0; while(*ar != EOF) { if(ispunct(*ar++) != 0) { count++; } } return count; } int digit_check(char *ar) { int count = 0; while(*ar != EOF) { if(isdigit(*ar++) != 0) { count++; } } return count; }
13、
#include <stdio.h> void revert(char *ar); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i = 0; for(i = 1; i < argc; i++) { printf("%s ", argv[argc - i]); } putchar('\n'); return 0; }

#include <stdio.h> void revert(char *ar); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i = 0; if(argc < 2) { puts("two few arguments"); } else { for(i = 1; i < argc; i++) { printf("%s ", argv[argc - i]); } putchar('\n'); } return 0; }

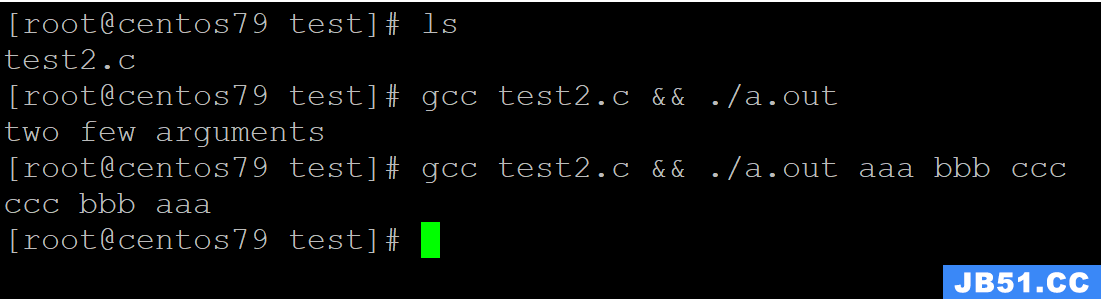
#include <stdio.h> void revert(char *ar); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i = 0; if(argc < 2) { puts("two few arguments"); } else { for(i = argc; i > 1; i--) { printf("%s ", argv[i - 1]); } putchar('\n'); } return 0; }
14、
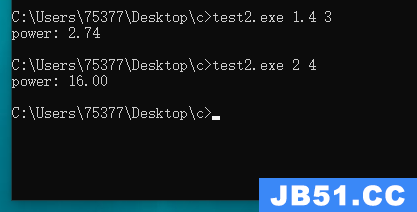
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int i; double power = 1.0; double argv_1 = atof(argv[1]); int argv_2 = atoi(argv[2]); if(argc != 3) { printf("argument error!"); } else { for(i = 0; i < argv_2; i++ ) power *= argv_1; } printf("power: %.2f\n", power); return 0; }
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int i; double power = 1.0; double argv_1 = atof(argv[1]); int argv_2 = atoi(argv[2]); if(argc != 3) { printf("argument error! only %d argument!\n", argc); return 0; } else { for(i = 0; i < argv_2; i++ ) power *= argv_1; } printf("power: %.2f\n", power); return 0; }

15、
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #define SIZE 100 int convert_int(char *ar); char *s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { int result; char st1[SIZE]; printf("st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); printf("result: %d\n",convert_int(st1)); return 0; } int convert_int(char *ar) { int i = 0; while(ar[i] != '\0' && isdigit(ar[i])) i++; if(ar[i] != '\0') { puts("not all digits!"); return 0; } else { int len = 0; while(ar[len] != '\0') len++; i = 0; int j; int temp; int result = 0; while(ar[i] != '\0') { temp = 1; int num = ar[i] - '0'; for(j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) { temp *= 10; } result = result + num * temp; i++; } return result; } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }


#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #define SIZE 100 int convert_int(char *ar); char *s_gets(char *st, int n); int main(void) { int result; char st1[SIZE]; printf("st1: "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); while(st1[0] != '\0') { printf("result: %d\n",convert_int(st1)); printf("st1(blank to quit): "); s_gets(st1, SIZE); } return 0; } int convert_int(char *ar) { int i = 0; while(ar[i] != '\0' && isdigit(ar[i])) i++; if(ar[i] != '\0') { puts("not all digits!"); return 0; } else { int len = 0; while(ar[len] != '\0') len++; i = 0; int j; int temp; int result = 0; while(ar[i] != '\0') { temp = 1; int num = ar[i] - '0'; for(j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) { temp *= 10; } result = result + num * temp; i++; } return result; } } char *s_gets(char *st, int n) { char *ret_val; int i = 0; ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin); if(ret_val) { while(st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0') i++; if(st[i] == '\n') st[i] = '\0'; else while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ret_val; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 int str_int(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); scanf("%s", st1); printf("convert result: %d\n", str_int(st1)); return 0; } int str_int(char *ar) { int len = 0; len = strlen(ar); int result = 0; int i; int temp = 1; for(i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if(isdigit(ar[i]) == 0) { puts("not all digit!"); return 0; } result = result + (ar[i] - '0') * temp; temp *= 10; } return result; }


循环:
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 int str_int(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); scanf("%s", st1); while(1) { printf("convert result: %d\n", str_int(st1)); printf("please input st1(q to quit): "); scanf("%s", st1); if(st1[0] == 'q') break; } return 0; } int str_int(char *ar) { int len = 0; len = strlen(ar); int result = 0; int i; int temp = 1; for(i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if(isdigit(ar[i]) == 0) { puts("not all digit!"); return 0; } result = result + (ar[i] - '0') * temp; temp *= 10; } return result; }
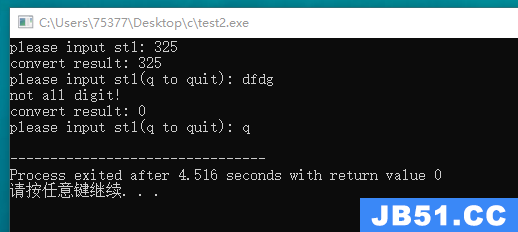
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 int convert(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); scanf("%s", st1); printf("convert result: %d\n", convert(st1)); return 0; } int convert(char *ar) { int len = strlen(ar); int i; int temp = 1; int result = 0; for(i = len; i > 0; i--) { if(isdigit(*(ar + i - 1)) == 0) { puts("not all digit!"); return 0; } result = result + (*(ar + i - 1) - '0') * temp; temp *= 10; } return result; }


循环:
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 100 int convert(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input st1: "); scanf("%s", st1); while(1) { printf("convert result: %d\n", convert(st1)); printf("please input st1(q to break): "); scanf("%s", st1); if(st1[0] == 'q') break; } return 0; } int convert(char *ar) { int len = strlen(ar); int i; int temp = 1; int result = 0; for(i = len; i > 0; i--) { if(isdigit(*(ar + i - 1)) == 0) { puts("not all digit!"); return 0; } result = result + (*(ar + i - 1) - '0') * temp; temp *= 10; } return result; }

16、
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> void to_upper(char *ar); void to_lower(char *ar); int main(void) { char st1[100] = "abCDEF"; puts("upper: "); to_upper(st1); puts("\nlower: "); to_lower(st1); return 0; } void to_upper(char *ar) { int i; while(*(ar + i)) { *(ar + i) = toupper(*(ar + i)); i++; } puts(ar); } void to_lower(char *ar) { int i; while(*(ar + i)) { *(ar + i) = tolower(*(ar + i)); i++; } puts(ar); }

16、
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 256 void printf_orig(char *st); void printf_upper(char *st); void printf_lower(char *st); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { char c; if(argc < 2) { c = 'p'; } else c = argv[1][1]; char test[SIZE]; printf("please input the string: "); fgets(test, SIZE, stdin); switch(c) { case 'p': case 'P': printf_orig(test); break; case 'u': case 'U': printf_upper(test); break; case 'l': case 'L': printf_lower(test); break; } return 0; } void printf_orig(char *st) { puts("result: "); puts(st); } void printf_upper(char *st) { int i = 0; while(*(st + i)) { *(st + i) = toupper(*(st + i)); i++; } puts("result: "); puts(st); } void printf_lower(char *st) { int i = 0; while(*(st + i)) { *(st + i) = tolower(*(st + i)); i++; } puts("result: "); puts(st); }

#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #define SIZE 256 void printf_orig(char *st); void printf_upper(char *st); void printf_lower(char *st); int main(char argc, char *argv[]) { char c; if(argc < 2) { c = 'p'; } else { c = argv[1][1]; } char test[SIZE]; printf("please input the string: "); fgets(test, SIZE, stdin); switch(c) { case 'p': case 'P': printf_orig(test); break; case 'u': case 'U': printf_upper(test); break; case 'l': case 'L': printf_lower(test); break; } return 0; } void printf_orig(char *st) { printf("origin: %s\n", st); } void printf_upper(char *st) { printf("upper: "); while(*st != EOF && *st != '\0') { putchar(toupper(*st++)); } putchar('\n'); } void printf_lower(char *st) { printf("lower: "); while(*st != EOF && *st != '\0') { putchar(tolower(*st++)); } putchar('\n'); }
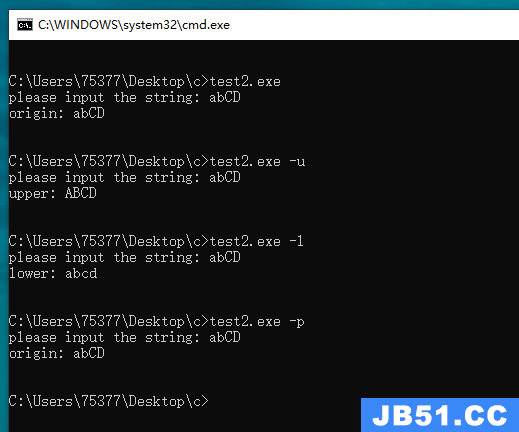
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #define SIZE 100 void print_orig(char *ar); void print_upper(char *ar); void print_lower(char *ar); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { char ch; if(argc < 2) { ch = 'p'; } else { ch = argv[1][1]; } char st1[SIZE]; printf("please input the string: "); fgets(st1, SIZE, stdin); switch(ch) { case 'p': case 'P': print_orig(st1); break; case 'u': case 'U': print_upper(st1); break; case 'l': case 'L': print_lower(st1); break; } return 0; } void print_orig(char *st) { printf("origin: %s\n", st); } void print_upper(char *st) { printf("upper: "); while(*st != '\0') { putchar(toupper(*st++)); } } void print_lower(char *st) { printf("lower: "); while(*st != '\0') { putchar(tolower(*st++)); } }

#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <ctype.h> #define SIZE 80 #define NUMBER 5 void show_menu(void); void input_string(int number, char st[][SIZE]); void print_original(int number, char st[][SIZE]); void print_ascii(int number, char st[][SIZE]); void print_length(int number, char st[][SIZE]); void print_words(int number, char st[][SIZE]); void sort_order(int number, int order[][2]); int get_word_length(char *input); int main(void) { char test[NUMBER][SIZE]; int selected; input_string(NUMBER, test); show_menu(); while(scanf("%d", &selected) != 1) { printf("please input intiger.\n"); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } while(selected != 5) { switch(selected) { case 1: print_original(NUMBER, test); break; case 2: print_ascii(NUMBER, test); break; case 3: print_length(NUMBER, test); break; case 4: print_words(NUMBER, test); break; case 5: break; default: printf("Error select, retry!\n"); } show_menu(); while(scanf("%d", &selected) != 1) { printf("please input intiger.\n"); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } } printf("All done, bye."); } void show_menu() { puts("================================================================\n"); printf("1) print original strings 2) print string by ascii order\n"); printf("3) print string by length 4) print string by word length\n"); printf("5) quit\n"); puts("\n==============================================================\n"); } void input_string(int number, char st[][SIZE]) { printf("please intput 5 strings seperate by enter.\n"); int i; for(i = 0; i < number; i++) { fgets(st[i], SIZE, stdin); } } void print_original(int number, char st[][SIZE]) { printf("print 5 strings in original mode.\n"); int i; for(i = 0; i < number; i++) { printf("%d %s", i, st[i]); } } void print_ascii(int number, char st[][SIZE]) { printf("print 5 strings in ascii order.\n"); int order[number][2]; int i; for(i = 0; i < number; i++) { order[i][0] = i; order[i][1] = st[i][0]; } sort_order(number, order); for(i = 0; i <number; i++) { printf("ASCII NO. %d. %s", i, st[order[i][0]]); } } void print_length(int number, char st[][SIZE]) { printf("print 5 strings in length mode.\n"); int order[number][2]; int i; for(i = 0; i < number; i++) { order[i][0] = i; order[i][1] = strlen(st[i]); } sort_order(number, order); for(i = 0; i < number; i++) { printf("length NO. %d. %s", i, st[order[i][0]]); } } void print_words(int number, char st[][SIZE]) { printf("print 5 strings in words mode\n"); int order[number][2]; int i; for(i = 0; i < number; i++) { order[i][0] = i; order[i][1] = get_word_length(st[i]); } sort_order(number, order); for(i = 0; i < number; i++) { printf("words NO. %d. %s", i, st[order[i][0]]); } } void sort_order(int number, int order[][2]) { int temp[2]; int i, j; for(i = 0; i < number - 1; i++) { for(j = 0; j < number - 1 - i; j++) { if(order[j][1] > order[j + 1][1]) { temp[0] = order[j][0]; temp[1] = order[j][1]; order[j][0] = order[j + 1][0]; order[j][1] = order[j + 1][1]; order[j + 1][0] = temp[0]; order[j + 1][1] = temp[1]; } } } } int get_word_length(char *input) { char *in = input; int length = 0; while(isalpha(*in) == 0) { in++; } while(isalpha(*in) != 0) { in++; length++; } return length; }

版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。

