1、
#include <stdio.h> void critic(int * ar1); int main(void) { int num; printf("how many pounds to a firkin of butter? \n"); scanf("%d", &num); while(num != 56) critic(&num); printf("you must have looked the answer!\n"); return 0; } void critic(int * ar1) { printf("wrong, try again!\n"); scanf("%d", ar1); }

#include <stdio.h> void critic(int * n); int main(void) { int units; printf("how many pounds to a firkin of butter?\n"); scanf("%d", &units); while(units != 56) critic(&units); printf("you must have looked it up!\n"); return 0; } void critic(int * n) { printf("No luck, my friends, try again.\n"); scanf("%d", n); }

2、
[root@centos79 test2]# cat pe12-2a.c #include <stdio.h> int mode; double distance; double fuel; void set_mode(int ar1) { if(ar1 > 1) { ar1 == 1; printf("Invalid mode specified. Mode 1(US) used.\n"); } } void get_info(void) { if(mode == 0) { printf("Enter distance traveled in kilometers: "); scanf("%lf", &distance); printf("Enter fuel consumed in liters: "); scanf("%lf", &fuel); } else { printf("Enter distance traveled in miles: "); scanf("%lf", &distance); printf("Enter fuel consumed in gallons: "); scanf("%lf", &fuel); } } void show_info(void) { if(mode == 0) { printf("Fuel xonsumption is %.2f liters per 100Km\n", fuel / distance * 100); } else { printf("Fuel consumption is %.2f miles per gallon.\n", distance / fuel); } }
[root@centos79 test2]# ls pe12-2a.c pe12-2a.h pe12-2b.c [root@centos79 test2]# cat pe12-2a.h extern int mode; extern double distance; extern double fuel; void set_mode(int ar); void get_info(void); void show_info(void);
[root@centos79 test2]# ls pe12-2a.c pe12-2a.h pe12-2b.c [root@centos79 test2]# cat pe12-2b.c #include <stdio.h> #include "pe12-2a.h" int main(void) { printf("enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode: "); scanf("%d", &mode); while(mode >= 0) { set_mode(mode); get_info(); show_info(); printf("enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for us mode"); printf(" (-1 to quit): "); scanf("%d", &mode); } return 0; }
[root@centos79 test2]# ls pe12-2a.c pe12-2a.h pe12-2b.c [root@centos79 test2]# gcc * [root@centos79 test2]# ls a.out pe12-2a.c pe12-2a.h pe12-2a.h.gch pe12-2b.c
[root@centos79 test2]# ls a.out pe12-2a.c pe12-2a.h pe12-2a.h.gch pe12-2b.c [root@centos79 test2]# ./a.out enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode: 0 Enter distance traveled in kilometers: 600 Enter fuel consumed in liters: 78.8 Fuel xonsumption is 13.13 liters per 100Km enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for us mode (-1 to quit): 1 Enter distance traveled in miles: 434 Enter fuel consumed in gallons: 12.7 Fuel consumption is 34.17 miles per gallon. enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for us mode (-1 to quit): 3 Invalid mode specified. Mode 1(US) used. Enter distance traveled in miles: 388 Enter fuel consumed in gallons: 15.3 Fuel consumption is 25.36 miles per gallon. enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for us mode (-1 to quit): -1
3、
[root@centos79 test2]# ls h.h x.c y.c [root@centos79 test2]# cat x.c #include <stdio.h> void set_mode(int * ar1) { if(*ar1 > 1) { printf("Invalid mode specified, Mode 1(US) used.\n"); *ar1 = 1; } } void get_info(int * ar1, double * ar2, double * ar3) { if(*ar1 == 0) { printf("Enter distance traveled in kilometer: "); scanf("%lf", ar2); printf("Enter fuel consumed in liters: "); scanf("%lf", ar3); printf("Fuel consumption is %.2f liters per 100 km.\n", *ar3 / *ar2 * 100); } else { printf("Enter distance traveled in miles: "); scanf("%lf", ar2); printf("Enter fule consumed in gallon: "); scanf("%lf", ar3); printf("Fuel consumption is %.2f mile per gallon.\n", *ar2 / *ar3); } }
[root@centos79 test2]# cat y.c #include <stdio.h> #include "h.h" int main(void) { while(1) { auto int mode; double distance, fuel; //自动变量 printf("Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode"); printf(" (-1 to quit): "); scanf("%d", &mode); if(mode < 0) break; set_mode(&mode); get_info(&mode, &distance, &fuel); } printf("Done,\n"); return 0; }
[root@centos79 test2]# cat h.h extern void set_mode(int * ar1); extern void get_info(int * ar1, double * ar2, double * ar3);
[root@centos79 test2]# ls h.h x.c y.c [root@centos79 test2]# gcc * [root@centos79 test2]# ls a.out h.h h.h.gch x.c y.c
[root@centos79 test2]# ls a.out h.h h.h.gch x.c y.c [root@centos79 test2]# ./a.out Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode (-1 to quit): 0 Enter distance traveled in kilometer: 600 Enter fuel consumed in liters: 78.8 Fuel consumption is 13.13 liters per 100 km. Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode (-1 to quit): 1 Enter distance traveled in miles: 434 Enter fule consumed in gallon: 12.7 Fuel consumption is 34.17 mile per gallon. Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode (-1 to quit): 3 Invalid mode specified, Mode 1(US) used. Enter distance traveled in miles: 388 Enter fule consumed in gallon: 15.3 Fuel consumption is 25.36 mile per gallon. Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode (-1 to quit): -1 Done,
4、
#include <stdio.h> int invoke(void); int times = 0; int main(void) { int i; for(i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { invoke(); } printf("times: %d\n", times); return 0; } int invoke(void) { printf("hello world!\n");; times++;
return times; }

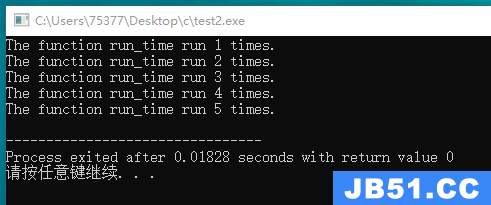
#include <stdio.h> static int count = 0; int run_counter(void); int main(void) { int i; for(i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { printf("The function run_time run %d times.\n", run_counter()); } return 0; } int run_counter(void) { return ++count; }
5、
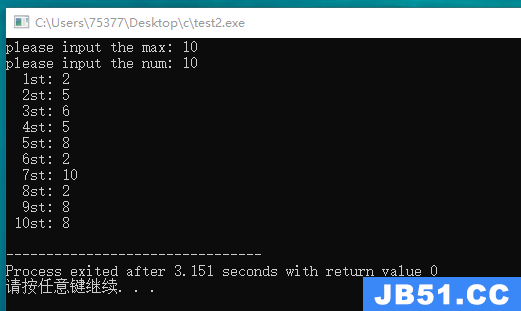
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { int max; int num; int i; printf("please input the max: "); scanf("%d", &max); printf("please input the num: "); scanf("%d", &num); srand((unsigned int) time(0)); for(i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { printf("%3dst: %d\n", i, rand() % 10 + 1); } return 0; }
#include <stdio.h> #define NUM 5 int main(void) { int ar1[] = {45,2, 4, 34, 23}; int i, j; int temp; for(i = 0; i < NUM - 1; i++) { for(j = i + 1; j < NUM; j++) { if(ar1[i] > ar1[j]) { temp = ar1[i]; ar1[i] = ar1[j]; ar1[j] = temp; } } } for(i = 0; i < NUM; i++) { printf("ar[%d]: %d\n", i + 1, ar1[i]); } return 0; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #define NUM 15 int main(void) { int i; int max; int ar1[NUM]; printf("please input max: "); scanf("%d", &max); srand((unsigned int) time(0)); for(i = 0; i < NUM; i++) { ar1[i] = rand() % max + 1; printf("%3dst: %d\n", i + 1, ar1[i]); } int j, temp; for(i = 0; i < NUM - 1; i++) { for(j = i + 1; j < NUM; j++) { if(ar1[i] < ar1[j]) { temp = ar1[i]; ar1[i] = ar1[j]; ar1[j] = temp; } } } puts("\n============================\n"); for(i = 0; i < NUM; i++) { printf("ar1[%d]: %d\n", i, ar1[i]); } return 0; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #define SIZE 10 void sort(int ar1[], int n); int main(void) { int i; int data[SIZE]; srand((unsigned int) time(0)); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { data[i] = rand() % 10 + 1; } printf("the original data is: \n"); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { printf("%4d\n", data[i]); } printf("\n"); puts("\n==============================\n"); sort(data, SIZE); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { printf("%4d\n", data[i]); } return 0; } void sort(int ar1[], int n) { int i, j; int temp; for(i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for(j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if(ar1[i] < ar1[j]) { temp = ar1[i]; ar1[i] = ar1[j]; ar1[j] = temp; } } } }

6、
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #define SIZE 10 int main(void) { int i, j; int data[10] = {0}; srand((unsigned int) time(0)); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { int temp; temp = rand() % 10 + 1; printf("temp: %d\n", temp); for(j = 0; j < 10; j++) { if(temp == j + 1) { data[j] += 1; } } } puts("\ncounts:\n"); for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) { printf("%d: %d\n", i + 1, data[i]); } return 0; }


#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #define SIZE 100 int main(void) { int i, j; int data[10] = {0}; srand((unsigned int) time(0)); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { int temp; temp = rand() % 10 + 1; //printf("temp: %d\n", temp); for(j = 0; j < 10; j++) { if(temp == j + 1) { data[j] += 1; } } } puts("\ncounts:\n"); for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) { printf("%d: %d\n", i + 1, data[i]); } return 0; }


#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #define SIZE 11 #define LEN 1000 int main(void) { int i, j; for(i = 1; i < SIZE; i++) { printf("%dst loop!\n", i); srand(i); int data[SIZE] = {0}; for(j = 0; j < LEN; j++) { int temp; temp = rand() % 10 + 1; data[temp]++; } for(j = 1; j < SIZE; j++) { printf("%d: %d\n", j, data[j]); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }

7、
[root@centos79 test2]# cat diceroll.c #include "diceroll.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> static int rollem(int sides) { int roll; roll = rand() % sides + 1; return roll; } int roll_n_dice(int dice, int sides) { int d; int total = 0; if(sides < 2) { printf("need at least 2 sides.\n"); return -2; } if(dice < 1) { printf("need at least 1 die.\n"); return -1; } for(d = 0; d < dice; d++) { total += rollem(sides); } return total; }
[root@centos79 test2]# cat diceroll.h int roll_n_dice(int dice, int sides);
[root@centos79 test2]# cat manydice.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include "diceroll.h" int main(void) { int dice, roll; int sides; int status; printf("enter the number of sets, enter q to stop: "); int loop; while(scanf("%d", &loop) == 1 && loop >= 1) { printf("how many sides and how many dice? "); if(scanf("%d", &sides) == 1 && sides > 0 && scanf("%d", &dice) == 1) { int i; for(i = 1; i <= loop ; i++) { srand(i * (unsigned int) time(0)); roll = roll_n_dice(dice, sides); if(i == 1) { printf("here are %d sets of %d %d-sides throws.\n", loop, dice, sides); } printf("%d ", roll); if(i % 15 == 0 || i == loop) { putchar('\n'); } } while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } else { printf("the sides should be positive integer, dice should be positive integer.\n"); printf("try again?"); } printf("how many sets? enter q to stop:"); } }
[root@centos79 test2]# ls diceroll.c diceroll.h manydice.c [root@centos79 test2]# gcc * [root@centos79 test2]# ls a.out diceroll.c diceroll.h diceroll.h.gch manydice.c
[root@centos79 test2]# ./a.out enter the number of sets, enter q to stop: 18 how many sides and how many dice? 6 3 here are 18 sets of 3 6-sides throws. 9 4 8 16 3 10 13 12 9 6 6 12 9 14 8 12 11 13 how many sets? enter q to stop:18 how many sides and how many dice? 6 3 here are 18 sets of 3 6-sides throws. 10 7 5 9 15 8 11 11 17 8 15 16 10 10 11 14 13 10 how many sets? enter q to stop:46 how many sides and how many dice? 6 3 here are 46 sets of 3 6-sides throws. 11 7 14 13 11 9 13 10 13 13 11 12 8 11 13 7 6 11 7 13 9 10 18 7 9 4 17 12 10 10 10 13 8 16 11 11 6 8 13 9 17 8 16 11 7 12 how many sets? enter q to stop:q
[root@centos79 test]# cat diceroll.c #include "diceroll.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int roll_count = 0; static int rollem(int sides) { int roll; roll = rand() % sides + 1; ++roll_count; return roll; } int roll_n_dice(int dice, int sides) { int d; int total = 0; if(sides < 2) { printf("need at lease 2 sides.\n"); return -2; } if(dice < 1) { printf("need at least 1 die.\n"); return -1; } for(d = 0; d < dice; d++) { total += rollem(sides); } return total; }
[root@centos79 test]# cat *.h extern int roll_count; int roll_n_dice(int dice, int sides);
[root@centos79 test]# cat manydice.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include "diceroll.h" int main(void) { int dice, roll; int sides; int set; srand((unsigned int) time(0)); printf("enter the number of sets; enter q to stop: "); while(scanf("%d", &set) == 1 && set > 0) { printf("how many sides and how many sice? "); if(scanf("%d %d", &sides, &dice) == 2 && sides > 0 && dice > 0) { printf("here are %d sets of %d %d-sided throws.\n", set, dice, sides); int i; for(i = 1; i <= set; i++) { roll = roll_n_dice(dice, sides); printf(" %d", roll); } set = 0; putchar('\n'); } printf("enter the number of sets; enter q to stop: "); } printf("count: %d\n", roll_count); return 0; }
[root@centos79 test]# ls diceroll.c diceroll.h manydice.c [root@centos79 test]# gcc * [root@centos79 test]# ls a.out diceroll.c diceroll.h diceroll.h.gch manydice.c
[root@centos79 test]# ./a.out enter the number of sets; enter q to stop: 18 how many sides and how many sice? 6 3 here are 18 sets of 3 6-sided throws. 13 15 7 7 11 16 11 14 10 9 11 12 12 8 10 10 7 13 enter the number of sets; enter q to stop: 5 how many sides and how many sice? 6 3 here are 5 sets of 3 6-sided throws. 14 11 8 8 9 enter the number of sets; enter q to stop: q count: 69
8、
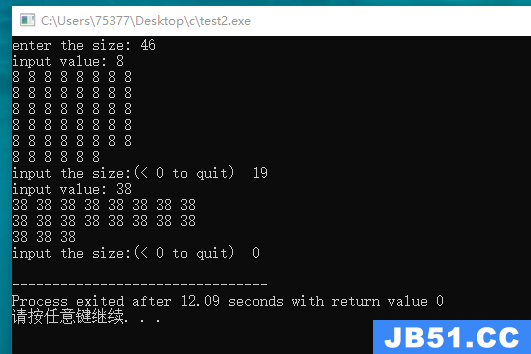
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int * make_array(int num, int val); void show_array(const ar[], int num); int main(void) { int * pa; int size; int value; printf("enter the size: "); while(scanf("%d", &size) == 1 && size > 0) { printf("input value: "); scanf("%d", &value); pa = make_array(size, value); if(pa) { show_array(pa, size); free(pa); } printf("input the size:(< 0 to quit) "); } return 0; } int * make_array(int num, int val) { int * temp = (int *) malloc(num * sizeof(int)); if(temp == NULL) { return NULL; } int i; for(i = 0; i < num; i++) { temp[i] = val; } return temp; } void show_array(const ar[], int num) { int i; for(i = 0; i < num; i++) { printf("%d ", ar[i]); if((i + 1) % 8 == 0) { putchar('\n'); } } putchar('\n'); }
9、
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int amount; printf("how may words do you wish to enter? "); scanf("%d", &amount); printf("enter %d words now: \n", amount); char **pst = (char **) malloc(amount * sizeof(char *)); int i; for(i = 0; i < amount; i++) { char temp[100]; scanf("%s", temp); int length = strlen(temp); char * str = (char *) malloc (length * sizeof(char)); strcpy(str, temp); *(pst + i) = str; } puts("\n=================\n"); for(i = 0; i < amount; i++) { printf("%s\n", *(pst + i)); } free(pst); printf("\nall done!\n"); return 0; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int num; printf("how many words: "); scanf("%d", &num); printf("enter %d num now: \n", num); char **pst = (char **) malloc(num * sizeof(char *)); int i; for(i = 0; i < num; i++) { char temp[100]; scanf("%s", temp); int length; length = strlen(temp); char *str = (char *) malloc(length * sizeof(char)); strcpy(str, temp); *(pst + i) = str; } puts("\n\n"); for(i = 0; i < num; i++) { printf("%s\n", *(pst + i)); } free(pst); return 0; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int num; int i; printf("please input the num: "); scanf("%d", &num); char ** ptd = (char **) malloc(num * sizeof(char *)); printf("now input the words:\n"); for(i = 0; i < num; i++) { char temp[44]; scanf("%s", temp); int length; length = strlen(temp); char * str = (char *) malloc(length * sizeof(char)); strcpy(str, temp); *(ptd + i) = str; } printf("now show the result: \n"); for(i = 0; i < num; i++) { printf("%s\n", ptd[i]); } free(ptd); return 0; }

版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。

