知音专栏
程序员的出路
写程序时该追求什么,什么是次要的?
如何准备Java初级和高级的技术面试
上一篇:手写spring+springmvc+mybatis框架篇【springIOC容器】
题外话:技术交流,欢迎加入QQ群:696209224 。广告勿扰!
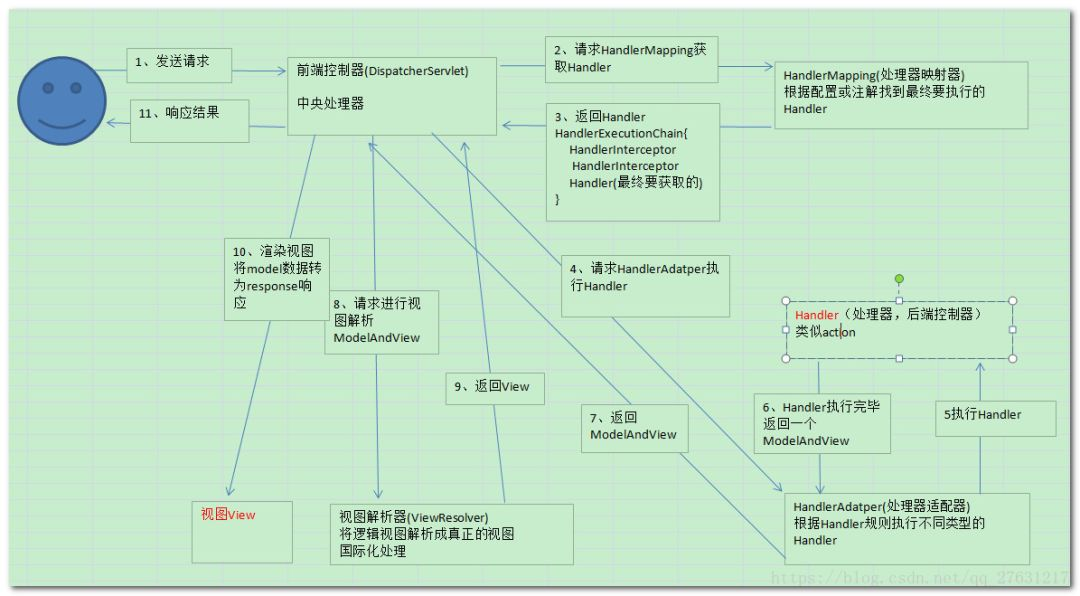
先放一张网上的很好的一张原理图
图片出自,这篇博客原理也写的很清晰明了。我的实现也是借鉴了这张图
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/6164383.html
先说一下我的实现思路:
1 在MydispatcherServlet中的servlet初始化的时候,绑定标有@MyController注解类下面的@MyRequestMappign的value值和对应的方法。绑定的方式是放在map集合中。这个map集合就是上图说的handlerMapping,返回的handler也就是一组键值对。
2 找到对应的方法后,反射执行方法,在方法中创建一个modelandview对象,model也就是我们说的数据域,view返回的是一个视图名称,也就是我们说的视图域,当然,我这里只有jsp,spring做的很复杂。支持多种类型。最后所谓的渲染,也就是将这个数据域中的数据会添加到request请求中,然后转发。返回客户端。
3 绑定参数模型这一部分略为复杂。在下面讲解
下面是MydispatcherServlet
这个servlet的作用就是接收用户请求,然后派发注意标红处bingdingMethodParamters方法,这个方法实现了参数的绑定。
package spring.servlet;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import spring.factory.InitBean;
import spring.springmvc.Binding;
import spring.springmvc.Handler;
import spring.springmvc.MyModelAndView;
import spring.springmvc.ViewResolver;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.servletexception;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import static spring.springmvc.BindingRequestAndModel.bindingRequestAndModel;
/**
* Created by Xiao Liang on 2018/6/27.
*/
@WebServlet(name = "MydispatcherServlet")
@Slf4j
public class MydispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
/**
* 初始化servlet,将bean容器和HandlerMapping放到servlet的全局变量中
*/
@Override
public void init() {
InitBean initBean = new InitBean();
initBean.initBeans();
//根据bean容器中注册的bean获得HandlerMapping
Map<String, Method> bindingRequestMapping = Handler.bindingRequestMapping(initBean.beanContainerMap);
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("beanContainerMap", initBean.beanContainerMap);
servletContext.setAttribute("bindingRequestMapping", bindingRequestMapping);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws servletexception, IOException {
try {
dodispatch(request, response);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("控制器处理异常");
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws servletexception, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
//接收到请求后转发到相应的方法上
private void dodispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, InvocationTargetException, illegalaccessexception, InstantiationException {
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
//获取扫描controller注解后url和方法绑定的mapping,也就是handlerMapping
Map<String, Method> bindingRequestMapping =
(Map<String, Method>) servletContext.getAttribute("bindingRequestMapping");
//获取实例化的bean容器
Map<String, Object> beanContainerMap = (Map<String, Object>) servletContext.getAttribute("beanContainerMap");
String url = request.getServletPath();
Set<Map.Entry<String, Method>> entries = bindingRequestMapping.entrySet();
List<Object> resultParameters = Binding.bingdingMethodParamters(bindingRequestMapping, request);
for (Map.Entry<String, Method> entry :
entries) {
if (url.equals(entry.getKey())) {
Method method = entry.getValue();
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
//如果返回值是MyModelAndView,开始绑定
if ("MyModelAndView".equals(returnType.getSimpleName())){
Object object = beanContainerMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
//获取springmvc.xml中配置的视图解析器
ViewResolver viewResolver = (ViewResolver) beanContainerMap.get("spring.springmvc.ViewResolver");
String prefix = viewResolver.getPrefix();
String suffix = viewResolver.getSuffix();
MyModelAndView myModelAndView = (MyModelAndView) method.invoke(object, resultParameters.toArray());
//将request和model中的数据绑定,也就是渲染视图
bindingRequestAndModel(myModelAndView,request);
String returnViewName = myModelAndView.getView();
//返回的路径
String resultAddress = prefix + returnViewName + suffix;
try {
request.getRequestdispatcher(resultAddress).forward(request,response);
} catch (servletexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
首先是绑定方法和url,是Handler类,用如下对象绑定
Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();package spring.springmvc;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import spring.Utils.AnnotationUtils;
import spring.annotation.MyController;
import spring.annotation.MyRequestMapping;
import spring.exception.springmvcException;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* @ClassName Handler
* @Description 遍历bean容器,在有controller注解的类中有requestmapping扫描的方法,则将方法和url和方法绑定
* @Data 2018/7/3
* @Author xiao liang
*/
@Slf4j
public class Handler {
public static Map<String, Method> bindingRequestMapping(Map<String, Object> beanContainerMap){
Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
if (beanContainerMap != null){
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entries = beanContainerMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry :
entries) {
Class aClass = entry.getValue().getClass();
Annotation annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(MyController.class);
Method[] methods = aClass.getmethods();
if (!AnnotationUtils.isEmpty(annotation) && methods != null){
for (Method method:
aClass.getmethods()) {
MyRequestMapping requestMappingAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
if (!AnnotationUtils.isEmpty(requestMappingAnnotation)){
String key = requestMappingAnnotation.value();
handlerMapping.put(key,method);
}
}
}
}
}
else{
throw new springmvcException("实例化bean异常,没有找到容器");
}
return handlerMapping;
}
}
参数绑定支持
下面先贴一下这一部分的结构关系图
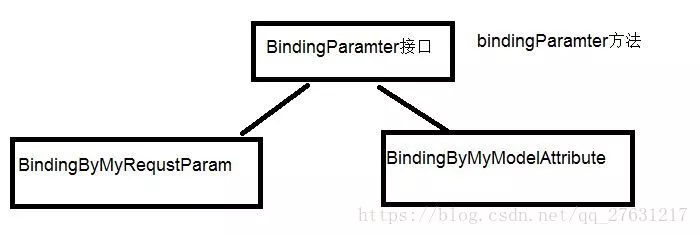
这里用多态的设计思想,对于bindingParamter方法写了两种实现,方便大家自行扩展
package spring.springmvc;
import spring.Utils.AnnotationUtils;
import spring.Utils.isBasicTypeUtils;
import spring.annotation.Mymodelattribute;
import spring.annotation.MyRequstParam;
import spring.exception.springmvcException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @ClassName Binding
* @Description
* @Data 2018/7/4
* @Author xiao liang
*/
public class Binding {
public static List<Object> bingdingMethodParamters(Map<String, Method> bindingRequestMapping, HttpServletRequest request) {
List<Object> resultParameters = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Map.Entry<String, Method>> entries = bindingRequestMapping.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Method> entry :
entries) {
Method method = entry.getValue();
Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
for (Parameter parameter :
parameters) { //遍历每个参数,如果参数存在注解,将这个参数添加到resultParameters中
if (!AnnotationUtils.isEmpty(parameter.getAnnotations())){
Object resultParameter = null;
try {
resultParameter = bingdingEachParamter(parameter, request);
} catch (illegalaccessexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
throw new springmvcException("绑定参数异常");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printstacktrace();
throw new springmvcException("绑定参数异常");
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printstacktrace();
throw new springmvcException("绑定参数异常");
}
resultParameters.add(resultParameter);
}
}
}
return resultParameters;
}
private static Object bingdingEachParamter(Parameter parameter, HttpServletRequest request) throws illegalaccessexception, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException {
//如果注解是MyRequstParam,则用BindingByMyRequstParam来执行装配
if (!AnnotationUtils.isEmpty(parameter.getAnnotation(MyRequstParam.class))){
BindingParamter bindingParamter = new BindingByMyRequstparam();
Object resultParameter = bindingParamter.bindingParamter(parameter, request);
return resultParameter;
}
//如果注解是Mymodelattribute,则用BindingByMymodelattribute来执行装配
else if (!AnnotationUtils.isEmpty(parameter.getAnnotation(Mymodelattribute.class))){
BindingParamter bindingParamter = new BindingByMymodelattribute();
Object resultParameter = bindingParamter.bindingParamter(parameter,request);
return resultParameter;
}
//在没有注解的时候,自动识别,如果是基本数据类型用MyRequstParam装配,如果是用户自定义类型用Mymodelattribute装配
else if(parameter.getAnnotations() == null || parameter.getAnnotations().length ==0){
boolean flag = isBasicTypeUtils.isBasicType(parameter.getType().getSimpleName());
if (flag){
BindingParamter bindingParamter = new BindingByMyRequstparam();
Object resultParameter = bindingParamter.bindingParamter(parameter, request);
return resultParameter;
}
else{
BindingParamter bindingParamter = new BindingByMymodelattribute();
Object resultParameter = bindingParamter.bindingParamter(parameter,request);
return resultParameter;
}
}
return null;
}
}下面是接口BindingParamter 和两个实现类BindingByMymodelattribute和BindingByMyRequstParam
package spring.springmvc;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
/**
* @ClassName BindingRoles
* @Description
* @Data 2018/7/4
* @Author xiao liang
*/
public interface BindingParamter {
Object bindingParamter(Parameter parameter, HttpServletRequest request) throws illegalaccessexception, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException;
}
package spring.springmvc;
import spring.Utils.StringUtils;
import spring.annotation.MyRequstParam;
import spring.exception.springmvcException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
/**
* @ClassName BindingByMyRequstParam
* @Description 参数注解是MyMyRequstParam时,绑定数据的类
* @Data 2018/7/4
* @Author xiao liang
*/
public class BindingByMyRequstParam implements BindingParamter {
@Override
public Object bindingParamter(Parameter parameter, HttpServletRequest request) {
MyRequstParam myRequstParam = parameter.getAnnotation(MyRequstParam.class);
//获得注解的value值
String MyRequstParamValue = myRequstParam.value();
//获得参数的类名
String parameterType = parameter.getType().getSimpleName();
String parameter1 = request.getParameter(MyRequstParamValue);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(parameter1)) {
throw new springmvcException("绑定参数异常");
}
//parameter1赋值
if (parameterType.equals("String")) {
return parameter1;
} else if (parameterType.equals("Integer") || parameterType.equals("int")) {
Integer binddingParameter = Integer.valueOf(parameter1);
return binddingParameter;
}
return null;
}
}package spring.springmvc;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import spring.Utils.AnnotationUtils;
import spring.Utils.ConvertUtis;
import spring.Utils.getmethodName;
import spring.Utils.StringUtils;
import spring.annotation.Mymodelattribute;
import spring.exception.springmvcException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
/**
* @ClassName BindingByMymodelattribute
* @Description 参数注解是Mymodelattribute时,绑定数据的类
* @Data 2018/7/4
* @Author xiao liang
*/
@Slf4j
public class BindingByMymodelattribute implements BindingParamter {
@Override
public Object bindingParamter(Parameter parameter, HttpServletRequest request) throws illegalaccessexception, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException {
Mymodelattribute mymodelattribute = parameter.getAnnotation(Mymodelattribute.class);
//获得参数的类名
Class<?> aClass = parameter.getType();
if (!AnnotationUtils.isEmpty(mymodelattribute)){
if (!aClass.getSimpleName().equals(mymodelattribute.value())){
throw new springmvcException("实体类绑定异常,请重新检查");
}
}
Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
Object object = aClass.newInstance();
//遍历每个属性,用set注入将值注入到对象中
for (Field field :
fields) {
//获得用户传来的值
String parameter1 = request.getParameter(field.getName());
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(parameter1)){
//将用户传过来的值转换成对应的参数类型
Object setobject = ConvertUtis.convert(field.getType().getSimpleName(),parameter1);
String methodName = getmethodName.getSetMethodNameByField(field.getName());
Method method = aClass.getmethod(methodName, field.getType());
try {
//反射set注入
method.invoke(object,setobject);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
log.error("{}属性赋值异常",field.getName());
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
//返回对注入值后的对象
return object;
}
}绑定完参数,就该返回ModelAndView了,
package spring.springmvc;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @ClassName MyModelAndView
* @Description
* @Data 2018/7/4
* @Author xiao liang
*/
@Data
public class MyModelAndView {
private String view;
private MyModelMap modelMap;
public MyModelAndView(String view) {
this.view = view;
}
}
view是视图名称,还有viewResolver,用来接收xml文件中定义的前缀和后缀。modelMap是数据域,最后渲染的时候要绑定到request中。
package spring.springmvc;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @ClassName ViewResolver
* @Description 视图解析器 前缀和后缀
* @Data 2018/7/4
* @Author xiao liang
*/
@Data
public class ViewResolver {
private String prefix = "";
private String suffix = "";
}最后的渲染类
package spring.springmvc;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @ClassName BindingRequestAndModel
* @Description
* @Data 2018/7/6
* @Author xiao liang
*/
public class BindingRequestAndModel {
//遍历modelMap,然后将model中的数据绑定到requst中
public static void bindingRequestAndModel(MyModelAndView myModelAndView, HttpServletRequest request) {
MyModelMap myModelMap = myModelAndView.getModelMap();
if (!myModelMap.isEmpty()){
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entries1 = myModelMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entryMap :
entries1) {
String key = entryMap.getKey();
Object value = entryMap.getValue();
request.setAttribute(key,value);
}
}
}
}至此,最后在MydispatcherServlet中用转发操作将试图返回。
request.getRequestdispatcher(resultAddress).forward(request,response);
我将此项目上传到了github,需要的童鞋可以自行下载。
https://github.com/836219171/MySSM
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 [email protected] 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。



