stepchain 介绍
stepchain 通用业务流程流水线处理框架。
类似于Commons Chain和Commons Pipeline这样的Java Pipeline Step Chain用于组织复杂处理流程执行的流行技术。
Java Pipeline Step Chain like Apache Commons Chain and Commons Pipeline。 A
popular technique for organizing the execution of complex processing flows is
the “Chain of Responsibility” pattern。
gitee: https://gitee.com/zengfr/stepchain
github: https://github.com/zengfr/stepchain-spring-boot-starter/
Repositories Central Sonatype
Mvnrepository
Feature: 1、支持通用业务job、services子流程无限制拆分。 2、支持业务子流程串行化、业务子流程并行化,可配置化。 3、支持Config业务子流程开启或禁用、配置串行或并行以及并行数的统一配置。 4、支持业务流程以及子流程任意无限嵌套。 5、支持配置中心、缓存、统一数据接口、redis、Es、日志Trace等。 6、支持并行分支,支持条件分支if/else、switch、loop子流程. 7、支持Processor定时调度Fixedrate、FixedDelay。 备注:只开源了通用部分(不影响使用),去除了有关框架组件包括:配置中心、缓存中心、数据接口以及业务相关DataMiddle等部分API。 Maven Dependency: Maven(Not Use Spring Boot): <dependency> <groupId>com.github.zengfr.project</groupId> <artifactId>stepchain</artifactId> <version>0.0.7</version> <dependency> Maven(Use Spring Boot): <dependency> <groupId>com.github.zengfr.project</groupId> <artifactId>stepchain-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>0.0.7</version> <dependency> Gradle: compile group: 'com.github.zengfr.project', name: 'stepchain', version: '0.0.7' compile group: 'com.github.zengfr.project', name: 'stepchain-spring-boot-starter', version: '0.0.7'
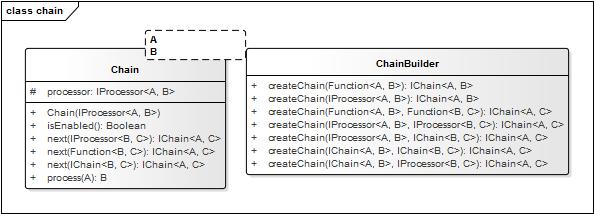
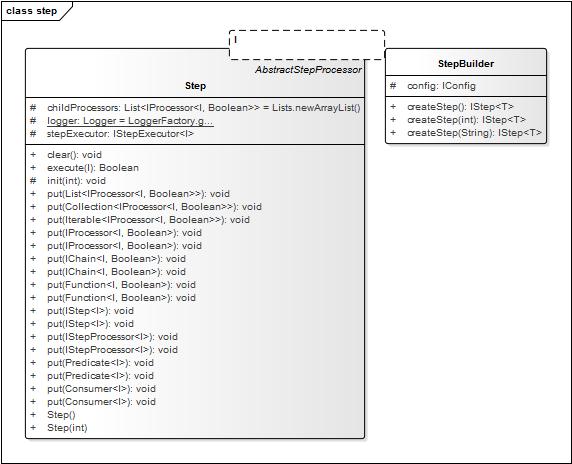
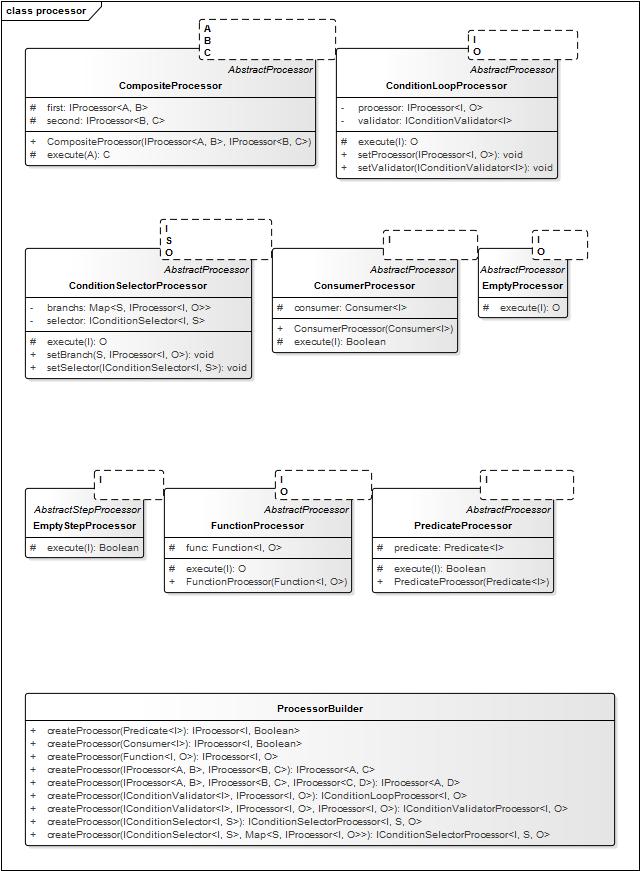
interface Pipeline ChainBuilder StepBuilder Step Chain javadoc
api文档

1、StepChain 的中心思想是什么?如何做到通用的? 答: 1.1、任何业务逻辑处理抽象成1\input输入 2\ processor处理器 3\output输出.中间过程结果产生和组合成dataMiddle。 1.2、任何业务逻辑处理使用多个processor组合执行。 2、StepChain 如何并行和串行执行多个processor? 答: 串行step=pipeline.createStep();step.put(processors);//processors串行执行. 并行step=pipeline.createStep(4);step.put(processors);//processors同时4个并行执行. 3、Stepchain 如何创建processor? 3.1、实现 IProcessor 接口。 3.2、使用IProcessorBuilder: <I> IProcessor<I, Boolean> createProcessor(Predicate<I> predicate); <I> IProcessor<I, Boolean> createProcessor(Consumer<I> consumer); <I, O> IProcessor<I, O> createProcessor(Function<I, O> func); 4、StepChain 如何复用和组合processor? 4.1、使用IChainBuilder、IChain: 4.2、使用IProcessorBuilder: <A, B, C> IProcessor<A, C> createProcessor(IProcessor<A, B> first, IProcessor<B, C> second); <A, B, C, D> IProcessor<A, D> createProcessor(IProcessor<A, B> processor1, IProcessor<B, C> processor2, IProcessor<C, D> processor3); 5、StepChain 如何按条件复用和组合processor? 答: case1、已有trueProcessor\falseProcessor2个 创建 validator 则按条件执行2则之1. IConditionSelectorProcessor<String, Boolean, String> p3 = pipeline.createConditionValidatorProcessor(validator, trueProcessor, falseProcessor); case2、已有processor 创建 validator 创建循环执行体,validator 返回false时终止执行。 IConditionLoopProcessor<String, String> p2 = pipeline.createConditionLoopProcessor(validator, processor); case3、已有processor创建 switch 逻辑,根据selector返回的key执行某1分支branchProcessor如果返回的key不在分支中 则执行默认key对应的分支branchProcessor。 IConditionSelectorProcessor<String, String, String> p1 = pipeline.createConditionSelectorProcessor(selector); p1.setBranch(S key, IProcessor<I, O> processor); p1setDefaultBranch(S key); case4、已有processor创建 if/else if/else 逻辑,根据validator返回的结果与result对比一致则执行分支branchProcessor,如果没有返回一致的 则执行默认分支branchProcessor。 pipeline.createConditionValidatorSelectorProcessor(); public interface IConditionValidatorSelectorProcessor<I,O> extends IProcessor<I, O> { void setBranch(IProcessor<I, Boolean> validator,Boolean result,IProcessor<I, O> processor); void setDefaultBranch(IProcessor<I, O> processor); } public interface IStep<I> extends IStepProcessor<I> { void put(IStepProcessor<I> processor); void put(IStepProcessor<I>... processorArray); void put(Collection<StepProcessor<I>> processors); void put(IProcessor<I, Boolean> processor); void put(IProcessor<I, Boolean>... processorArray); void put(IChain<I, Boolean> chain); void put(IChain<I, Boolean>... processorArray); void put(Function<I, Boolean> func); void put(Function<I, Boolean>... processorArray); } public interface IChain<A, B> extends IProcessor<A, B> { <C> IChain<A, C> next(IProcessor<B, C> process); <C> IChain<A, C> next(Function<B, C> func); } public interface IChainBuilder { <A, B> IChain<A, B> createChain(Function<A, B> func); <A, B> IChain<A, B> createChain(IProcessor<A, B> processor); <A, B, C> IChain<A, C> createChain(IProcessor<A, B> processor1, IProcessor<B, C> processor2); } public interface IStepBuilder { <T> IStep<T> createStep(); <T> IStep<T> createStep(int parallelCount); <T> IStep<T> createStep(String parallelCountConfigName); }
PipelineTest.java
Demo&Test you can use AbstractProcessor AbstractStepProcessor
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain
abstract class AbstractProcessor<I, O> implements Processor<I, O>{}
abstract class AbstractStepProcessor<A> extends AbstractProcessor<A, Boolean> implements StepProcessor<A>{}
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.Chain;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.Pipeline;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.Step;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.context.ContextBuilder;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.context.UnaryContext;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.test.context.SetProductContext;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.test.context.SetProductDataMiddle;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.test.processor.discountProcessor;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.test.processor.FeeProcessor;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.test.processor.IncreaseProcessor;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.test.processor.InitProcessor;
import com.github.zengfr.project.stepchain.test.processor.TaxProcessor;
public class PipelineTest {
public static void testPipeline(IPipeline pipeline) throws Exception {
//Demo精简版 只开源了通用部分(不影响使用)
SetProductRequest req = new SetProductRequest();
SetProductResponse resp = new SetProductResponse();
SetProductDataMiddle middle = new SetProductDataMiddle();
SetProductContext context = new SetProductContext(req, middle, resp);
IStep<SetProductContext> step = pipeline.createStep();
step.put(new InitProcessor());
step.put(new TaxProcessor());
step.put(new FeeProcessor());
step.put(new IncreaseProcessor());
step.put(new discountProcessor());
step.put((c) -> {
c.middle.Price += 10;
return true;
});
step.process(context);
System.out.println(context.middle.Price);
}
public static void testPipeline2(IPipeline pipeline) throws Exception {
Function<UnaryContext<Integer>, Boolean> func = (context) -> {
if (context.context == null)
context.context = 1;
context.context += 1;
return true;
};
Function<UnaryContext<Integer>, String> func3 = (context) -> {
if (context.context == null)
context.context = 1;
context.context += 1;
return JSON.toJSONString(context.context);
};
UnaryContext<Integer> context = pipeline.createContext(12345678);
IStep<UnaryContext<Integer>> step = pipeline.createStep();
IStep<UnaryContext<Integer>> step2 = pipeline.createStep();
IChain<UnaryContext<Integer>, Boolean> c2 = pipeline.createChain(func);
IChain<UnaryContext<Integer>, String> c3 = pipeline.createChain(func3);
Function<String, Integer> func4 = null;
Function<Integer, String> func5 = null;
Function<String, Boolean> func6 = null;
IChain<String,Integer > c4 = pipeline.createChain(func4);
IChain<Integer, String> c5 = pipeline.createChain(func5);
IChain<String, Boolean> c6 = pipeline.createChain(func6);
IChain<UnaryContext<Integer>, Boolean> c7 = c3.next(c4).next(c5).next(c6);
step2.put(c2);
step2.put(step);
step2.put(func);
//step2.put(c7);
step2.process(context);
System.out.println(context.context);
}
public static void testPipeline3(IPipeline pipeline) throws Exception {
IProcessor<String, String> selector = null;
IProcessor<String, Boolean> validator = null;
IProcessor<String, String> processor = null;
IProcessor<String, String> first = null;
IProcessor<String, String> second = null;
IConditionSelectorProcessor<String, Boolean, String> p3 = pipeline.createConditionValidatorProcessor(validator, first, second);
IConditionLoopProcessor<String, String> p2 = pipeline.createConditionLoopProcessor(validator, processor);
IConditionSelectorProcessor<String, String, String> p1 = pipeline.createConditionSelectorProcessor(selector);
}
@RunWith(springrunner.class)
@SpringBoottest(classes = StepChainTestApplication.class)
public class StepChainspringBoottest {
@Autowired
protected IPipeline pipeline;
@Test
public void testPipeline() throws Exception {
PipelineTest.testPipeline(pipeline);
}
@Test
public void testPipeline2() throws Exception {
PipelineTest.testPipeline2(pipeline);
}


stepchain 官网
https://gitee.com/zengfr/stepchain
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。




