开始
继续接着分析Flutter相关的样式和布局控件,但是这次内容难度感觉比较高,怕有分析不到位的地方,所以这次仅仅当做一个参考,大家最好可以自己阅读一下代码,应该会有更深的体会。
Sliver布局
Flutter存在着两大布局体系(就目前分析),一个是Box布局,还有另外一个就是Sliver布局;但是Sliver布局明显比Box会更加复杂,这真是一个坎,那么为啥说Sliver更加复杂尼,请看一下对比:
首先是Box布局,主要看输入的BoxConstraints(约束)和输出Size(尺寸)
class BoxConstraints extends Constraints {
const BoxConstraints({
this.minWidth: 0.0,
this.maxWidth: double.infinity,
this.minHeight: 0.0,
this.maxHeight: double.infinity
});
}class Size extends OffsetBase {
const Size(double width, double height) : super(width, height);
}而Sliver布局,SliverConstraints(约束)和输出SliverGeometry
class SliverConstraints extends Constraints {
const SliverConstraints({
@required this.axisDirection,
@required this.growthDirection,
@required this.userScrollDirection,
@required this.scrollOffset,
@required this.overlap,
@required this.remainingPaintExtent,
@required this.crossAxisExtent,
@required this.crossAxisDirection,
@required this.viewportMainAxisExtent,
})
}class SliverGeometry extends Diagnosticable {
const SliverGeometry({
this.scrollExtent: 0.0,
this.paintExtent: 0.0,
this.paintOrigin: 0.0,
double layoutExtent,
this.maxPaintExtent: 0.0,
this.maxScrollObstructionExtent: 0.0,
double hitTestExtent,
bool visible,
this.hasVisualOverflow: false,
this.scrollOffsetCorrection,
})
}两者一对比,Box布局明显参数更少,也更直观:maxWidth,width,minWidth这些一看就明白其起到的作用;但是Sliver布局无论输入输出都是一大堆参数,这些参数究竟起到什么作用,为什么需要这些参数,不看代码真的很难明白。
Viewport组件
其实介绍Sliver布局,必须得先介绍Viewport组件,因为Sliver相关组件需要在Viewport组件下使用,而Viewport组件的主要作用就是提供滚动机制,可以根据传入的offset参数来显示特定的内容;在Flutter中并不像web只需在每个元素样式上加上overflow: auto,元素内容就可以自动滚动,这是因为Flutter主要一个思想就是万物皆组件,无论样式还是布局或者功能都是以组件形式出现。
class Viewport extends MultiChildRenderObjectWidget {
Viewport({
Key key,
this.axisDirection: AxisDirection.down, //主轴方向,默认往下
this.crossAxisDirection, //纵轴方向
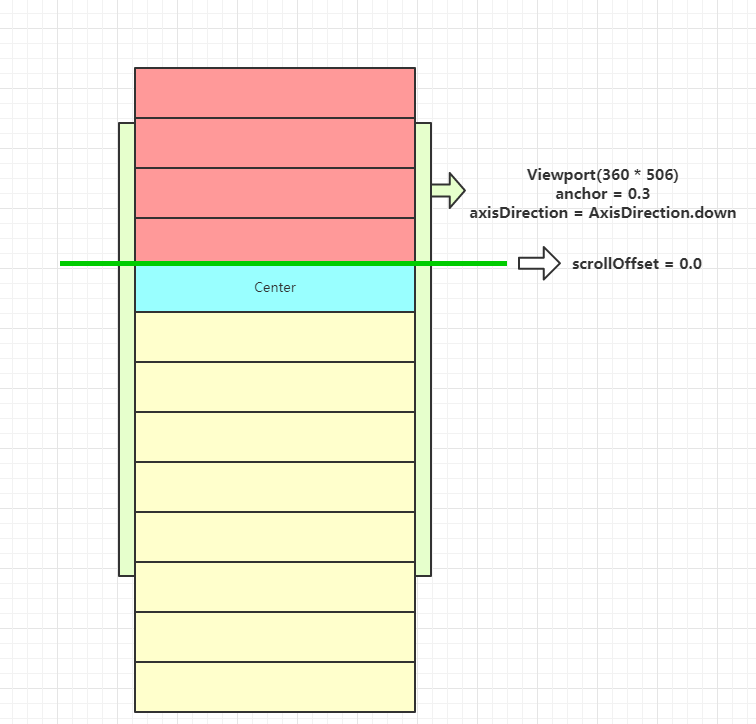
this.anchor: 0.0, //决定scrollOffset = 0分割线在viewport的位置(0 <= anchor <= 1.0)
@required this.offset, //viewport偏移位置
this.center, //标记哪个作为center组件
List<Widget> slivers: const <Widget>[], //sliver组件双向列表
})
}虽然简单描述了各个参数的作用,但是还是不够直观。。。还是画图吧:
首先上图整个可以看到Center参数的作用可以标出整个列表应该以哪个组件为基线来布局,Center组件始终在scrollOffset = 0.0的初始线上开始布局,而anchor参数则可以控制scrollOffset = 0.0这个初始线在Viewport上的位置,这里设置的是0.3,所以初始线的位置是距离顶端506 * .3 = 151.8这个位置上放置的。
虽然这样好像把参数的作用都搞清楚了,但是仍然没有知道为什么需要这些参数,继续深入RenderViewport,了解一下布局的核心。
直接跳到performLayout方法:
void performLayout() {
...
final double centerOffsetAdjustment = center.centerOffsetAdjustment;
double correction;
int count = 0;
do {
assert(offset.pixels != null);
correction = _attemptLayout(mainAxisExtent, crossAxisExtent, offset.pixels + centerOffsetAdjustment);
if (correction != 0.0) {
offset.correctBy(correction);
} else {
if (offset.applyContentDimensions(
math.min(0.0, _minScrollExtent + mainAxisExtent * anchor),
math.max(0.0, _maxScrollExtent - mainAxisExtent * (1.0 - anchor)),
))
break;
}
count += 1;
} while (count < _kMaxLayoutCycles);这里可以注意到performLayout里面存在一个循环,只要哪个元素布局的过程中需要调整滚动的偏移量,就会更新滚动偏移量之后再重新布局,但是重新布局的次数不能超过_kMaxLayoutCycles也就是10次,这里也是明显从性能考虑;
另外Center组件还有一个centerOffsetAdjustment属性,例如centerOffsetAdjustment为50.0的时候,Center组件就会再原来基础上往上50.0,但是这里的处理可以看到只是等同于改变了滚动偏移量,增加50.0的偏移位置,所做到的效果。
然后直接把Viewport的宽高和调整后的滚动偏移量传入_attemptLayout方法:
double _attemptLayout(double mainAxisExtent, double crossAxisExtent, double correctedOffset) {
_minScrollExtent = 0.0;
_maxScrollExtent = 0.0;
_hasVisualOverflow = false;
final double centerOffset = mainAxisExtent * anchor - correctedOffset;
final double clampedForwardCenter = math.max(0.0, math.min(mainAxisExtent, centerOffset));
final double clampedReverseCenter = math.max(0.0, math.min(mainAxisExtent, mainAxisExtent - centerOffset));
final RenderSliver leadingNegativeChild = childBefore(center);
if (leadingNegativeChild != null) {
// negative scroll offsets
final double result = layoutChildSequence(
leadingNegativeChild,
math.max(mainAxisExtent, centerOffset) - mainAxisExtent,
0.0,
clampedReverseCenter,
clampedForwardCenter,
mainAxisExtent,
crossAxisExtent,
GrowthDirection.reverse,
childBefore,
);
if (result != 0.0)
return -result;
}
// positive scroll offsets
return layoutChildSequence(
center,
math.max(0.0, -centerOffset),
leadingNegativeChild == null ? math.min(0.0, -centerOffset) : 0.0,
clampedForwardCenter,
clampedReverseCenter,
mainAxisExtent,
crossAxisExtent,
GrowthDirection.forward,
childAfter,
);
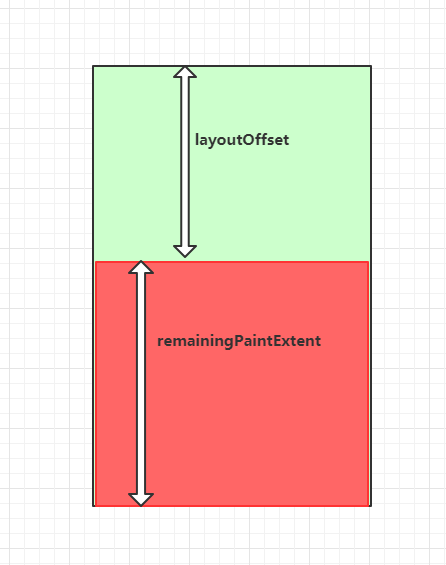
}这里先提前说一下两个关键属性layoutOffset和remainingPaintExtent:
layoutOffset表示组件在Viewport中偏移多少距离才开始布局,而remainingPaintExtent表示在Viewport中剩余绘制区域大小,一旦remainingPaintExtent为0的时候,控件是不需要绘制的,因为就算绘制了用户也看不到。
而这几行代码:
final double centerOffset = mainAxisExtent * anchor - correctedOffset;
final double clampedForwardCenter = math.max(0.0, math.min(mainAxisExtent, centerOffset));
final double clampedReverseCenter = math.max(0.0, math.min(mainAxisExtent, mainAxisExtent - centerOffset));就是计算这两个关键属性过程,可以假设centerOffset为0.0的时候,clampedForwardCenter就等于0.0,clampedReverseCenter 等于 mainAxisExtent;所以也就等于layoutOffset等于0.0,remainingPaintExtent等于mainAxisExtent。
接着分析,当Center组件前面还有组件的时候,就会进入刚才代码的处理流程:
if (leadingNegativeChild != null) {
// negative scroll offsets
final double result = layoutChildSequence(
leadingNegativeChild,
math.max(mainAxisExtent, centerOffset) - mainAxisExtent,
0.0,
clampedReverseCenter,
clampedForwardCenter,
mainAxisExtent,
crossAxisExtent,
GrowthDirection.reverse,
childBefore,
);
if (result != 0.0)
return -result;
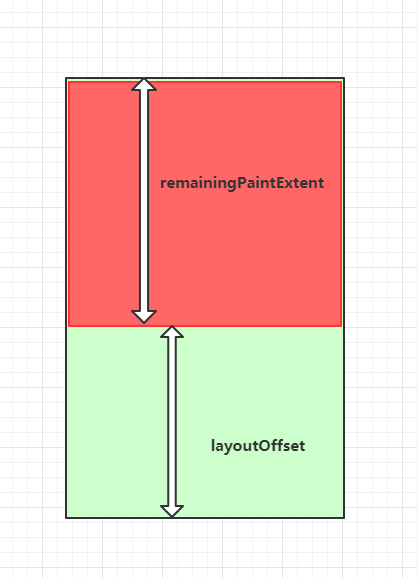
}Center前面的组件会一个接一个布局,但是对于Center前面的组件,刚才描述layoutOffset和remainingPaintExtent的图得要倒着来看,也就是说会变成这样:
所以Center组件其实就是一个分割线把内容分成上下两部分,一部分顺着Viewport主轴方向,另外一部分是反主轴的方向发展的,再看看layoutChildSequence方法:
double layoutChildSequence(
RenderSliver child,
double scrollOffset,
double overlap,
double layoutOffset,
double remainingPaintExtent,
double mainAxisExtent,
double crossAxisExtent,
GrowthDirection growthDirection,
RenderSliver advance(RenderSliver child),
) {
assert(scrollOffset.isFinite);
assert(scrollOffset >= 0.0);
final double initialLayoutOffset = layoutOffset;
final ScrollDirection adjustedUserScrollDirection =
applyGrowthDirectionToScrollDirection(offset.userScrollDirection, growthDirection);
assert(adjustedUserScrollDirection != null);
double maxPaintOffset = layoutOffset + overlap;
while (child != null) {
assert(scrollOffset >= 0.0);
child.layout(new SliverConstraints(
axisDirection: axisDirection,
growthDirection: growthDirection,
userScrollDirection: adjustedUserScrollDirection,
scrollOffset: scrollOffset,
overlap: maxPaintOffset - layoutOffset,
remainingPaintExtent: math.max(0.0, remainingPaintExtent - layoutOffset + initialLayoutOffset),
crossAxisExtent: crossAxisExtent,
crossAxisDirection: crossAxisDirection,
viewportMainAxisExtent: mainAxisExtent,
), parentUsesSize: true);
final SliverGeometry childLayoutGeometry = child.geometry;
assert(childLayoutGeometry.debugAssertIsValid());
// If there is a correction to apply, we'll have to start over.
if (childLayoutGeometry.scrollOffsetCorrection != null)
return childLayoutGeometry.scrollOffsetCorrection;
// We use the child's paint origin in our coordinate system as the
// layoutOffset we store in the child's parent data.
final double effectiveLayoutOffset = layoutOffset + childLayoutGeometry.paintOrigin;
updateChildLayoutOffset(child, effectiveLayoutOffset, growthDirection);
maxPaintOffset = math.max(effectiveLayoutOffset + childLayoutGeometry.paintExtent, maxPaintOffset);
scrollOffset -= childLayoutGeometry.scrollExtent;
layoutOffset += childLayoutGeometry.layoutExtent;
if (scrollOffset <= 0.0)
scrollOffset = 0.0;
updateOutOfBandData(growthDirection, childLayoutGeometry);
// move on to the next child
child = advance(child);
}
// we made it without a correction, whee!
return 0.0;
}这个方法比较长,而且没法精简了。
scrollOffset属性表示超出Viewport边界的距离,这里可以看到传进来的scrollOffset是必须大于等于0,也就是说scrollOffset其实等同于web的scrollTop属性了,但是如果scrollOffset大于0的时候,layoutOffset必然是等于0,remainingPaintExtent必然等于mainAxisExtent,只要联想一下刚才的图的就可以推出他们的关系了。
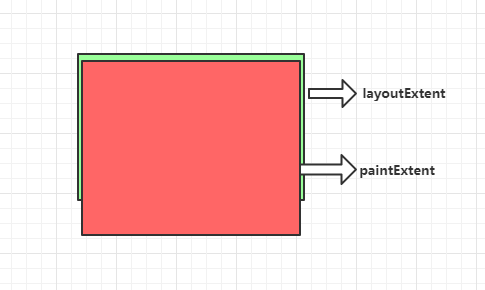
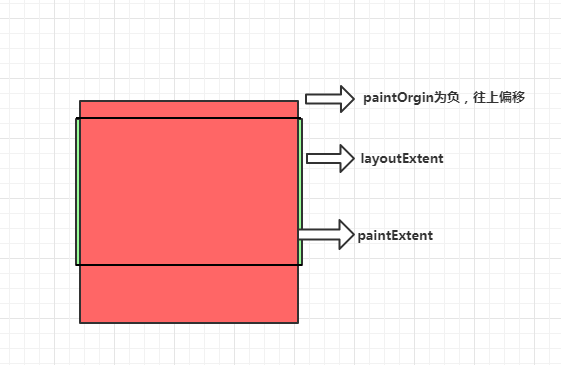
关于SliverConstraints.overlap属性,指前一个Sliver组件的layoutExtent(布局区域)和paintExtent(绘制区域)重叠了。
这里红色部分比绿色部分多出地方及时overlap的大小
但是也受SliverGeometry.paintOrigin影响,所以必须计算在内:
所以这里计算是这样:首先layoutOffset + paintOrigin + paintExtent = maxPaintOffset;再layoutOffset += layoutExtent;最后maxPintOffset - layoutOffset = 下个sliver的overlap。
final double effectiveLayoutOffset = layoutOffset + childLayoutGeometry.paintOrigin;
maxPaintOffset = math.max(effectiveLayoutOffset + childLayoutGeometry.paintExtent, maxPaintOffset);
scrollOffset -= childLayoutGeometry.scrollExtent;
layoutOffset += childLayoutGeometry.layoutExtent;而layoutOffset不停增加,最终导致remainingPaintExtent变成0.0,也就是告诉Sliver无需绘制了,而remainingPaintExtent为0.0的Sliver,最终计算的SliverGeometry的paintExtent和layoutExtent一般都是0.0,唯有scrollExtent不能为0.0,因为这个值需要加起来,决定下次是否能够继续滚动。
还有SliverGeometry.scrollOffsetCorrection属性的作用,这个值只要返回不是0.0,就会触发Viewport根据这个值修正偏移量后重新布局(这里存在的一个用途可能是滑动翻页的时候每次都能定位每一页的开始)
结束?
当然没有,下次接着写,Sliver布局还有挺多可以挖掘的地方,今天先到这里。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 [email protected] 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。