第1章 SparkStreaming 概述
Spark Streaming 用于流式数据的处理。
Spark Streaming 的特点
易用,容错,易整合到Spark 体系
Spark Streaming 架构
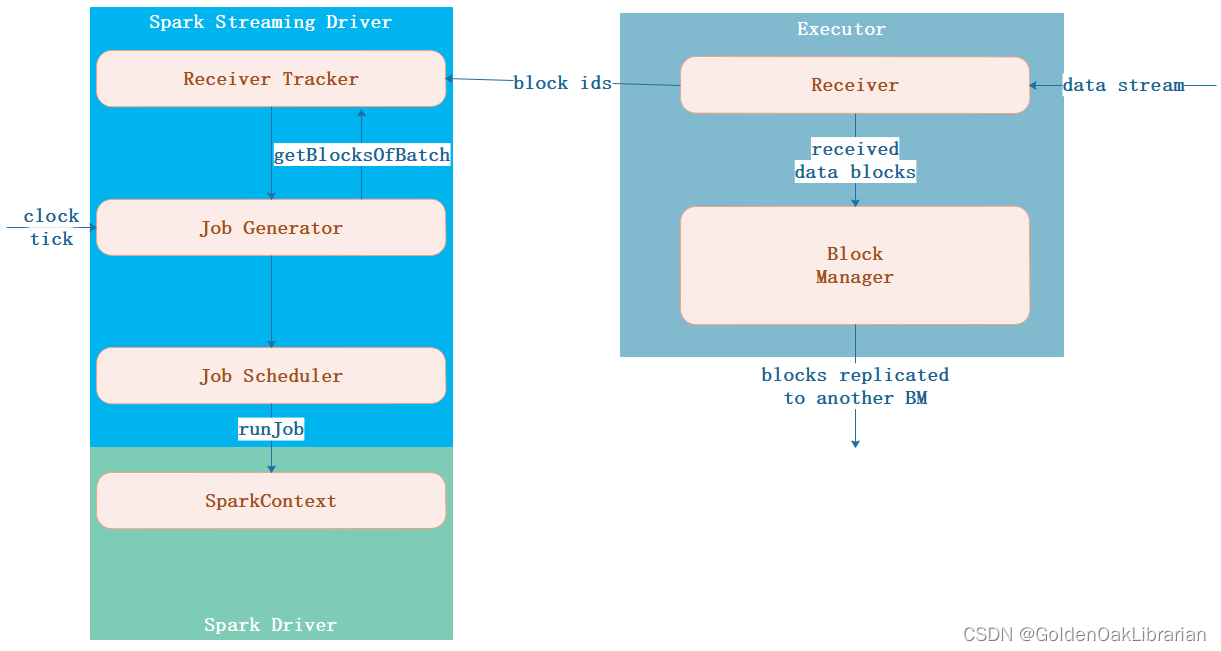
背压机制
背压机制(即 Spark Streaming Backpressure): 根据JobScheduler 反馈作业的执行信息来动态调整Receiver 数据接收率。
第 2 章 Dstream 入门
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming_2.12</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
- 编写代码
object StreamWordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1.初始化 Spark 配置信息
val sparkConf = new
SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("StreamWordCount")
//2.初始化 SparkStreamingContext
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(3))
//3.通过监控端口创建 DStream,读进来的数据为一行行
val lineStreams = ssc.socketTextStream("hadoop102", 9999)
//将每一行数据做切分,形成一个个单词
val wordStreams = lineStreams.flatMap(_.split(" "))
//将单词映射成元组(word,1)
val wordAndOneStreams = wordStreams.map((_, 1))
//将相同的单词次数做统计
val wordAndCountStreams = wordAndOneStreams.reduceByKey(_+_)
//打印
wordAndCountStreams.print()
//启动 SparkStreamingContext
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}
第 3 章 DStream 创建
3.1 RDD 队列
object RDDStream {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
//1.初始化 Spark 配置信息 (保留节目)
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("RDDStream")
//2.初始化 SparkStreamingContext (保留节目)
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(4))
//3.创建 RDD 队列
val rddQueue = new mutable.Queue[RDD[Int]]()
//4.创建 QueueInputDStream
val inputStream = ssc.queueStream(rddQueue,oneAtATime = false)
//5.处理队列中的 RDD 数据
//5.1 (word,1)
val mappedStream = inputStream.map((_,1))
//5.2 计算n(word,n)
val reducedStream = mappedStream.reduceByKey(_ + _)
//6.打印结果
reducedStream.print()
//7.启动任务
ssc.start()
//8.循环创建并向 RDD 队列中放入 RDD
for (i <- 1 to 5) {
rddQueue += ssc.sparkContext.makeRDD(1 to 300, 10)
Thread.sleep(2000)
}
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}
3.2 自定义数据源
class CustomerReceiver(host: String, port: Int) extends Receiver[String](StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY) {
//最初启动的时候,调用该方法,作用为:读数据并将数据发送给 Spark
override def onStart(): Unit = {
new Thread("Socket Receiver") {
override def run() {
receive()
}
}.start()
}
//读数据并将数据发送给 Spark
def receive(): Unit = {
//创建一个 Socket
var socket: Socket = new Socket(host, port)
//定义一个变量,用来接收端口传过来的数据
var input: String = null
//创建一个 BufferedReader 用于读取端口传来的数据
val reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream,
StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
//读取数据
input = reader.readLine()
//当 receiver 没有关闭并且输入数据不为空,则循环发送数据给 Spark
while (!isStopped() && input != null) {
store(input)
input = reader.readLine()
}
//跳出循环则关闭资源
reader.close()
socket.close()
//重启任务
restart("restart")
}
override def onStop(): Unit = {}
}
使用自定义的数据源采集数据
object FileStream {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//1.初始化 Spark 配置信息
val sparkConf = new SparkConf()
.setMaster("local[*]")
.setAppName("StreamWordCount")
//2.初始化 SparkStreamingContext
//def this(conf: SparkConf, batchDuration: Duration) = {
// this(StreamingContext.createNewSparkContext(conf), null, batchDuration)
// }
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(5))
//3.创建自定义 receiver 的 Streaming
//new PluggableInputDStream[T](this, receiver)
val lineStream = ssc.receiverStream(new CustomerReceiver("hadoop102", 9999))
//4.将每一行数据做切分,形成一个个单词
val wordStream = lineStream.flatMap(_.split("\t"))
//5.将单词映射成元组(word,1)
val wordAndOneStream = wordStream.map((_, 1))
//6.将相同的单词次数做统计
val wordAndCountStream = wordAndOneStream.reduceByKey(_ + _)
//7.打印
wordAndCountStream.print()
//8.启动 SparkStreamingContext
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}
3.3 Kafka 数据源
3.3.1 版本选型
ReceiverAPI:
- 需要一个专门的Executor 去接收数据,然后发送给其他的Executor 做计算。
- 存在的问题:接收数据的Executor 和计算的Executor 速度会有所不同,特别在接收数据的Executor速度大于计算的Executor 速度,会导致计算数据的节点内存溢出。
- 早期版本中提供此方式,当前版本不适用
DirectAPI:是由计算的Executor 来主动消费Kafka 的数据,速度由自身控制。
3.3.2 Kafka 0-8 Receiver 模式(当前版本不适用)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming-kafka-0-8_2.11</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>
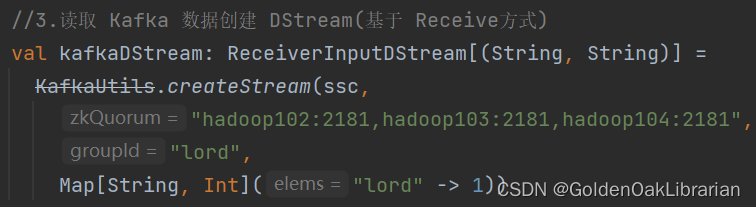
3.3.3 Kafka 0-8 Direct 模式(当前版本不适用)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming-kafka-0-8_2.11</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>
手动维护offset
//6.创建一个数组用于存放当前消费数据的 offset 信息
var offsetRanges = Array.empty[OffsetRange]
//7.获取当前消费数据的 offset 信息
val wordToCountDStream: DStream[(String, Int)] = kafkaDStream.transform { rdd
=>
offsetRanges = rdd.asInstanceOf[HasOffsetRanges].offsetRanges
rdd
}.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.map((_, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
//8.打印 Offset 信息
wordToCountDStream.foreachRDD(rdd => {
for (o <- offsetRanges) {
println(s"${o.topic}:${o.partition}:${o.fromOffset}:${o.untilOffset}")
}
rdd.foreach(println)
})
==3.3.4 Kafka 0-10 Direct 模式 ==
关键代码
//4.读取 Kafka 数据创建 DStream
val kafkaDStream: InputDStream[ConsumerRecord[String, String]] =
KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String](ssc,
LocationStrategies.PreferConsistent,
ConsumerStrategies.Subscribe[String, String](Set("atguigu"), kafkaPara))
//5.将每条消息的 KV 取出
val valueDStream: DStream[String] = kafkaDStream.map(record => record.value())
KafkaUtils的createDirectStream方法源码
/**
* Scala constructor for a DStream where
* each given Kafka topic/partition corresponds to an RDD partition.
* The spark configuration spark.streaming.kafka.maxRatePerPartition gives the maximum number
* of messages
* per second that each '''partition''' will accept.
* @param locationStrategy In most cases, pass in [[LocationStrategies.PreferConsistent]],
* see [[LocationStrategies]] for more details.
* @param consumerStrategy In most cases, pass in [[ConsumerStrategies.Subscribe]],
* see [[ConsumerStrategies]] for more details
* @tparam K type of Kafka message key
* @tparam V type of Kafka message value
*/
def createDirectStream[K, V](
ssc: StreamingContext,
locationStrategy: LocationStrategy,
consumerStrategy: ConsumerStrategy[K, V]
): InputDStream[ConsumerRecord[K, V]] = {
val ppc = new DefaultPerPartitionConfig(ssc.sparkContext.getConf)
createDirectStream[K, V](ssc, locationStrategy, consumerStrategy, ppc)
}
查看Kafka 消费进度
bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh --describe --bootstrap-server hadoop102:9092 --group lord
第 4 章 DStream 转换
4.1 无状态转化操作
无状态转化操作就是把简单的 RDD 转化操作应用到每个批次上,也就是转化DStream 中的每一个RDD。
| 函数名称 | 目的 | Scala示例 |
|---|---|---|
| map() | 对Dstream中的每个元素应用给定函数,返回输出的DStream | ds.map(x=>x+1) |
| flatMap() | 对Dstream中的每个元素应用给定函数,返回输出的DStream | ds.flatMap(x=>x.split(" ")) |
| filter() | 返回通过筛选的元素组成的DStream | ds.filter(x=>x!=1) |
| repartition() | 改变DStream的分区数 | ds.repartition(10) |
| reduceByKey() | 将每个批次中键相同的记录归约 | ds.reduceByKey((x,y)=>x+1) |
| groupByKey() | 将每个批次中的记录根据键分组 | ds.groupByKey() |
4.1.1 transform
Transform
- 允许DStream 上执行任意的RDD-to-RDD 函数。即使这些函数并没有在DStream的 API 中暴露出来
- 通过该函数可以方便的扩展Spark API
- 该函数每一批次调度一次。其实也就是对DStream 中的RDD 应用转换。
关键代码
//转换为 RDD 操作
val wordAndCountDStream: DStream[(String, Int)] = lineDStream.transform(rdd =>
{
val words: RDD[String] = rdd.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordAndOne: RDD[(String, Int)] = words.map((_, 1))
val value: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordAndOne.reduceByKey(_ + _)
value
})
transform源码
/**
* Return a new DStream in which each RDD is generated by applying a function on each RDD of 'this' DStream.
* 返回一个新DStream,在其中的每个RDD 是原DStream中RDD通过函数转换后的结果
*/
def transform[U: ClassTag](transformFunc: RDD[T] => RDD[U]): DStream[U] = ssc.withScope {
// because the DStream is reachable from the outer object here, and because DStreams can't be serialized with closures,
//we can't proactively check it for serializability and so we pass the optional false to SparkContext.clean
val cleanedF = context.sparkContext.clean(transformFunc, false)
transform((r: RDD[T], _: Time) => cleanedF(r))
}
transform追踪:发现返回TransformedDStream
/**
* Return a new DStream in which each RDD is generated by applying a function
* on each RDD of 'this' DStream.
*/
def transform[U: ClassTag](transformFunc: (RDD[T], Time) => RDD[U]): DStream[U] = ssc.withScope {
// because the DStream is reachable from the outer object here, and because
// DStreams can't be serialized with closures, we can't proactively check
// it for serializability and so we pass the optional false to SparkContext.clean
val cleanedF = context.sparkContext.clean(transformFunc, false)
val realTransformFunc = (rdds: Seq[RDD[_]], time: Time) => {
assert(rdds.length == 1)
cleanedF(rdds.head.asInstanceOf[RDD[T]], time)
}
new TransformedDStream[U](Seq(this), realTransformFunc)
}
追踪TransformedDStream:发现继承了DStream
class TransformedDStream[U: ClassTag] (
parents: Seq[DStream[_]],
transformFunc: (Seq[RDD[_]], Time) => RDD[U]
) extends DStream[U](parents.head.ssc)
4.1.2 join
- 两个流之间的join 需要两个流的批次大小一致,这样才能做到同时触发计算。
- 计算过程就是对当前批次的两个流中各自的RDD 进行 join,与两个 RDD 的join 效果相同。
//4.将两个流转换为 KV 类型
val wordToOneDStream: DStream[(String, Int)] = lineDStream1.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1))
val wordToADStream: DStream[(String, String)] = lineDStream2.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, "a"))
//5.流的 JOIN
val joinDStream: DStream[(String, (Int, String))] =
wordToOneDStream.join(wordToADStream)
join源码:调用join[W](other, defaultPartitioner())
/**
* Return a new DStream by applying 'join' between RDDs of `this` DStream and `other` DStream.
* Hash partitioning is used to generate the RDDs with Spark's default number of partitions.
*/
def join[W: ClassTag](other: DStream[(K, W)]): DStream[(K, (V, W))] = ssc.withScope {
join[W](other, defaultPartitioner())
}
join源码:可按需要传入Partitioner
/**
* Return a new DStream by applying 'join' between RDDs of `this` DStream and `other` DStream.
* The supplied org.apache.spark.Partitioner is used to control the partitioning of each RDD.
*/
def join[W: ClassTag](
other: DStream[(K, W)],
partitioner: Partitioner
): DStream[(K, (V, W))] = ssc.withScope {
self.transformWith(
other,
// 发现还是下到RDD
(rdd1: RDD[(K, V)], rdd2: RDD[(K, W)]) => rdd1.join(rdd2, partitioner)
)
}
4.2 有状态转化操作
4.2.1 UpdateStateByKey
UpdateStateByKey 原语用于记录历史记录
场景:有时,我们需要在 DStream 中跨批次维护状态(例如流计算中累加wordcount)。针对这种情况,updateStateByKey()为我们提供了对一个状态变量的访问,用于键值对形式的 DStream。
初始:给定一个由(键,事件)对构成的 DStream,
条件:并传递一个指定如何根据新的事件更新每个键对应状态的函数,
结果:它可以构建出一个新的 DStream,其内部数据为(键,状态) 对。
updateStateByKey 操作使得我们可以在用新信息进行更新时保持任意的状态。
为使用这个功能,需要做:
- 定义状态,状态可以是一个任意的数据类型。
- 定义状态更新函数,用此函数阐明如何使用之前的状态和来自输入流的新值对状态进行更新。
- 使用updateStateByKey 需要对检查点目录进行配置,会使用检查点来保存状态。
示例:由(键,事件)对构成的 DStream
//import org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext._ // not necessary since Spark 1.3
// Count each word in each batch
val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
示例:一个指定如何根据新的事件更新每个键对应状态的函数
// 定义更新状态方法,参数 values 为当前批次单词频度,state 为以往批次单词频度
val updateFunc = (values: Seq[Int], state: Option[Int]) => {
//当前批次单词频度计数
val currentCount = values.foldLeft(0)(_ + _)
//以往批次单词频度计数
val previousCount = state.getOrElse(0)
//加和
Some(currentCount + previousCount)
}
示例:调用UpdateStateByKey,构建出一个新的 DStream
// 使用 updateStateByKey 来更新状态,统计从运行开始以来单词总的次数
val stateDstream = pairs.updateStateByKey[Int](updateFunc)
updateStateByKey源码(传入参数完整版)
def updateStateByKey[S: ClassTag](
updateFunc: (Iterator[(K, Seq[V], Option[S])]) => Iterator[(K, S)],
partitioner: Partitioner,
rememberPartitioner: Boolean): DStream[(K, S)] = ssc.withScope {
val cleanedFunc = ssc.sc.clean(updateFunc)
val newUpdateFunc = (_: Time, it: Iterator[(K, Seq[V], Option[S])]) => {
cleanedFunc(it)
}
new StateDStream(self, newUpdateFunc, partitioner, rememberPartitioner, None)
}
返回的StateDStream
class StateDStream[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, S: ClassTag](
parent: DStream[(K, V)],
updateFunc: (Time, Iterator[(K, Seq[V], Option[S])]) => Iterator[(K, S)],
partitioner: Partitioner,
preservePartitioning: Boolean,
initialRDD: Option[RDD[(K, S)]]
) extends DStream[(K, S)](parent.ssc)
4.2.2 WindowOperations
- Window Operations 可以设置窗口的大小和滑动窗口的间隔来动态的获取当前Steaming 的允许状态。
- 所有基于窗口的操作都需要两个参数,分别为窗口时长以及滑动步长。
➢ 窗口时长:计算内容的时间范围;
➢ 滑动步长:隔多久触发一次计算。
注意:这两者都必须为采集周期大小的整数倍。
val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKeyAndWindow((a:Int,b:Int) => (a +
b),Seconds(12), Seconds(6))
/**
* Return a new DStream by applying `reduceByKey` over a sliding window. Similar to
* `DStream.reduceByKey()`, but applies it over a sliding window.
* @param reduceFunc associative and commutative reduce function
* @param windowDuration width of the window; must be a multiple of this DStream's
* batching interval
* @param slideDuration sliding interval of the window (i.e., the interval after which
* the new DStream will generate RDDs); must be a multiple of this
* DStream's batching interval
* @param partitioner partitioner for controlling the partitioning of each RDD
* in the new DStream.
*/
def reduceByKeyAndWindow(
reduceFunc: (V, V) => V,
windowDuration: Duration,
slideDuration: Duration,
partitioner: Partitioner
): DStream[(K, V)] = ssc.withScope {
self.reduceByKey(reduceFunc, partitioner)
.window(windowDuration, slideDuration)
.reduceByKey(reduceFunc, partitioner)
}
def window(windowDuration: Duration, slideDuration: Duration): DStream[T] = ssc.withScope {
new WindowedDStream(this, windowDuration, slideDuration)
}
class WindowedDStream[T: ClassTag](
parent: DStream[T],
_windowDuration: Duration,
_slideDuration: Duration)
extends DStream[T](parent.ssc)
关于Window 的操作还有如下方法:
(1)window(windowLength, slideInterval): 基于对源DStream 窗化的批次进行计算返回一个新的Dstream;
(2)countByWindow(windowLength, slideInterval): 返回一个滑动窗口计数流中的元素个数;
(3)reduceByWindow(func, windowLength, slideInterval): 通过使用自定义函数整合滑动区间流元素来创建一个新的单元素流;
(4)reduceByKeyAndWindow(func, windowLength, slideInterval, [numTasks]): 当在一个(K,V)对的DStream 上调用此函数,会返回一个新(K,V)对的 DStream,此处通过对滑动窗口中批次数据使用reduce 函数来整合每个 key 的value 值。
(5)reduceByKeyAndWindow(func, invFunc, windowLength, slideInterval, [numTasks]): 这个函数是上述函数的变化版本,每个窗口的reduce 值都是通过用前一个窗的 reduce 值来递增计算。通过reduce 进入到滑动窗口数据并”反向 reduce”离开窗口的旧数据来实现这个操作。
第 5 章 DStream 输出
- 输出操作指定了对流数据经转化操作得到的数据所要执行的操作。
- 与RDD 中的惰性求值类似,如果一个DStream 及其派生出的DStream 都没有被执行输出操作,那么这些DStream 就都不会被求值。
- 如果 StreamingContext 中没有设定输出操作,整个context 就都不会启动。
输出操作如下:
➢ print():
在运行流程序的驱动结点上打印DStream 中每一批次数据的最开始 10 个元素。这用于开发和调试。
在 Python API 中,同样的操作叫 print()。
➢ saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix]):
以text 文件形式存储这个 DStream 的内容。每一批次的存储文件名基于参数中的 prefix 和suffix。
➢ saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix]):
以Java 对象序列化的方式将 Stream 中的数据保存为 SequenceFiles . 每一批次的存储文件名基于参数中的为"prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]".
Python中目前不可用。
➢ saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix]):
将Stream 中的数据保存为 Hadoop files. 每一批次的存储文件名基于参数中的为"prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]"。
Python API 中目前不可用。
➢ foreachRDD(func):
这是最通用的输出操作,即将函数 func 用于产生于 stream 的每一个RDD。其中参数传入的函数 func 应该实现将每一个RDD 中数据推送到外部系统,如将RDD 存入文件或者通过网络将其写入数据库。
第 6 章 优雅关闭
流式任务需要 7*24 小时执行,但是有时涉及到升级代码需要主动停止程序,但是分布式程序,没办法做到一个个进程去杀死,所以我们要做到优雅的关闭。
MonitorStop
代码示例:
val bool: Boolean = fs.exists(new Path("hdfs://linux1:9000/stopSpark"))
if (bool) {
if (state == StreamingContextState.ACTIVE) {
ssc.stop(stopSparkContext = true, stopGracefully = true)
System.exit(0)
}
}
源码:查看stop()方法,发现其中调用了scheduler.stop()
Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
scheduler.stop(stopGracefully)
}
scheduler.stop如下
def stop(processAllReceivedData: Boolean): Unit = synchronized {
if (eventLoop == null) return // scheduler has already been stopped
logDebug("Stopping JobScheduler")
if (receiverTracker != null) {
// First, stop receiving
// 首先,停止receiving
receiverTracker.stop(processAllReceivedData)
}
if (executorAllocationManager != null) {
executorAllocationManager.foreach(_.stop())
}
// Second, stop generating jobs. If it has to process all received data,
// 其次,停止generating jobs
// then this will wait for all the processing through JobScheduler to be over.
// 这会得到jobGenerator中的processing 都结束
jobGenerator.stop(processAllReceivedData)
// Stop the executor for receiving new jobs
// 然后,使jobExecutor停止接收新任务
logDebug("Stopping job executor")
jobExecutor.shutdown()
// Wait for the queued jobs to complete if indicated
// 如果优雅,则在挺长一段时间里面慢慢关,如果不优雅就马上shutdown
val terminated = if (processAllReceivedData) {
jobExecutor.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS) // just a very large period of time
} else {
jobExecutor.awaitTermination(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
}
if (!terminated) {
jobExecutor.shutdownNow()
}
logDebug("Stopped job executor")
// Stop everything else
// 最后,把listenerBus,eventLoop也给停了
listenerBus.stop()
eventLoop.stop()
eventLoop = null
logInfo("Stopped JobScheduler")
}
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。

