前文传送门:
mybatis源码学习:从SqlSessionFactory到代理对象的生成
mybatis源码学习:一级缓存和二级缓存分析
mybatis源码学习:基于动态代理实现查询全过程
一、自定义插件流程
-
自定义插件,实现Interceptor接口。
-
实现intercept、plugin和setProperties方法。
-
使用@Intercepts注解完成插件签名。
-
在主配置文件注册插件。
/**
* 自定义插件
* Intercepts:完成插件签名,告诉mybatis当前插件拦截哪个对象的哪个方法
*
* @author Summerday
*/
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,method = "parameterize",args = Statement.class)
})
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {
/**
* 拦截目标方法执行
*
* @param invocation
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
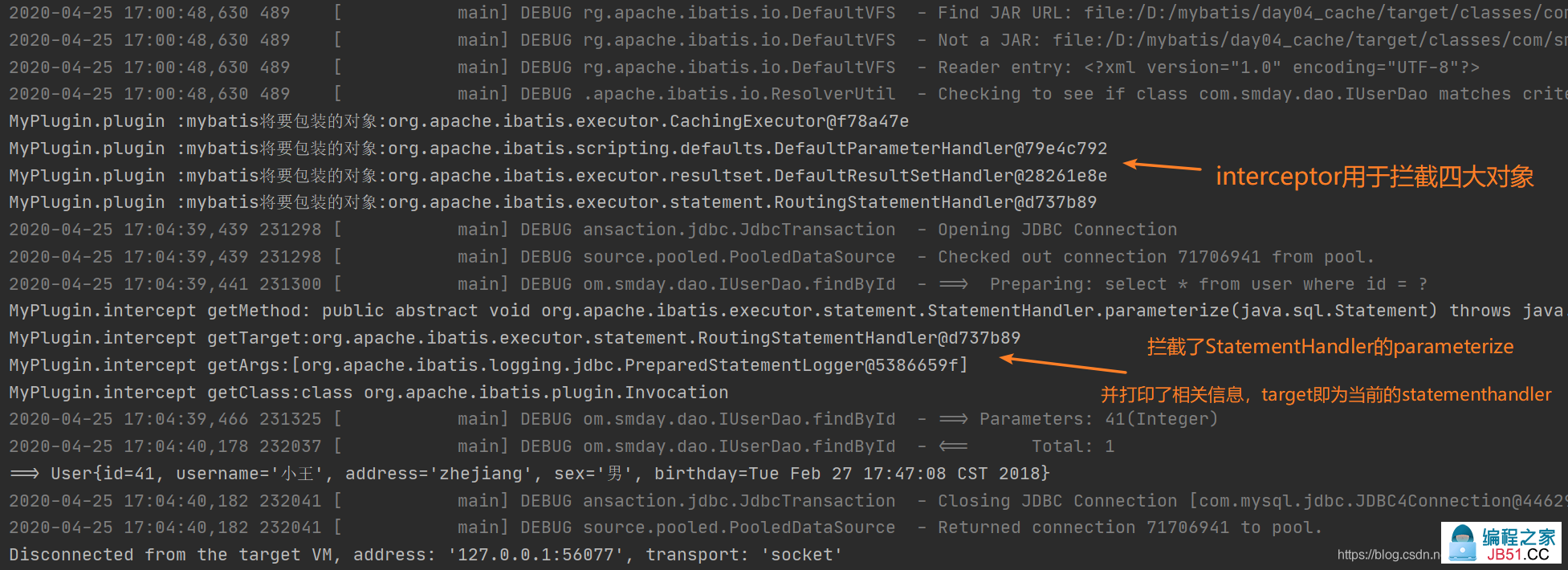
System.out.println("MyPlugin.intercept getMethod: "+invocation.getMethod());
System.out.println("MyPlugin.intercept getTarget:"+invocation.getTarget());
System.out.println("MyPlugin.intercept getArgs:"+ Arrays.toString(invocation.getArgs()));
System.out.println("MyPlugin.intercept getClass:"+invocation.getClass());
//执行目标方法
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
//返回执行后的返回值
return proceed;
}
/**
* 包装目标对象,为目标对象创建一个代理对象
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
System.out.println("MyPlugin.plugin :mybatis将要包装的对象:"+target);
//借助Plugin类的wrap方法使用当前拦截器包装目标对象
Object wrap = Plugin.wrap(target,this);
//返回为当前target创建的动态代理
return wrap;
}
/**
* 将插件注册时的properties属性设置进来
*
* @param properties
*/
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("插件配置的信息:" + properties);
}
}
xml配置注册插件
<!--注册插件-->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.smday.interceptor.MyPlugin">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
二、测试插件
三、源码分析
1、inteceptor在Configuration中的注册
关于xml文件的解析,当然还是需要从XMLConfigBuilder中查找,我们很容易就可以发现关于插件的解析:
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//获取到全类名
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
//获取properties属性
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
//通过反射创建实例
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
//设置属性
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
//在Configuration中添加插件
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
//interceptorChain是一个存储interceptor的Arraylist
interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
此时初始化成功,我们在配置文件中定义的插件,已经成功加入interceptorChain。
2、基于责任链的设计模式
我们看到chain这个词应该并不会陌生,我们之前学习过的过滤器也存在类似的玩意,什么意思呢?我们以Executor为例,当创建Executor对象的时候,并不是直接new Executor然后返回:

在返回之前,他进行了下面的操作:
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
我们来看看这个方法具体干了什么:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
//遍历所有的拦截器
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
//调用plugin,返回target包装后的对象
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
很明显,现在它要从chain中一一取出interceptor,并依次调用各自的plugin方法,暂且不谈plugin的方法,我们就能感受到责任链的功能:让一个对象能够被链上的任何一个角色宠幸,真好。
3、基于动态代理的plugin
那接下来,我们就成功进入我们自定义plugin的plugin方法:

//看看wrap方法干了点啥
public static Object wrap(Object target,Interceptor interceptor) {
//获取获取注解的信息,拦截的对象,拦截的方法,拦截方法的参数。
Map<Class<?>,Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
//获取当前对象的Class
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
//确认该对象是否为我们需要拦截的对象
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type,signatureMap);
//如果是,则创建其代理对象,不是则直接将对象返回
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),interfaces,new Plugin(target,interceptor,signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
getSignatureMap(interceptor)方法:其实就是获取注解的信息,拦截的对象,拦截的方法,拦截方法的参数。
private static Map<Class<?>,Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
//定位到interceptor上的@Intercepts注解
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
//如果注解不存在,则报错
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
//获取@Signature组成的数组
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>,Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>,Set<Method>>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
//先看map里有没有methods set
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
//没有再创建一个
methods = new HashSet<Method>();
//class:methods设置进去
signatureMap.put(sig.type(),methods);
}
try {
//获取拦截的方法
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(),sig.args());
//加入到set中
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e,e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
getAllInterfaces(type,signatureMap)方法:确定是否为拦截对象
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type,Map<Class<?>,Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
while (type != null) {
//接口类型
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
//如果确实是拦截的对象,则加入interfaces set
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
//从父接口中查看
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
//最后set里面存在的元素就是要拦截的对象
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
我们就可以猜测,插件只会对我们要求的对象和方法进行拦截。
4、拦截方法的intercept(invocation)
确实,我们一路debug,遇到了Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultHandler都没有进行拦截,然而,当StatementHandler对象出现的时候,就出现了微妙的变化,当我们调用代理的方法必然会执行其invoke方法,不妨来看看:

ok,此时进入了我们定义的intercept方法,感觉无比亲切。

//调度被代理对象的真实方法
public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException,IllegalAccessException {
return method.invoke(target,args);
}
如果有多个插件,每经过一次wrap都会产生上衣个对象的代理对象,此处反射调用的方法也是上衣个代理对象的方法。接着,就还是执行目标的parameterize方法,但是当我们明白这些执行流程的时候,我们就可以知道如何进行一些小操作,来自定义方法的实现了。
四、插件开发插件pagehelper
插件文档地址:https://github.com/pagehelper/Mybatis-PageHelper
这款插件使分页操作变得更加简便,来一个简单的测试如下:
1、引入相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2</version>
</dependency>
2、全局配置
<!--注册插件-->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin>
</plugins>
3、测试分页
@Test
public void testPlugin(){
//查询第一页,每页3条记录
PageHelper.startPage(1,3);
List<User> all = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : all) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}

五、插件总结
参考:《深入浅出MyBatis技术原理与实战》
- 插件生成地是层层代理对象的责任链模式,其中设计反射技术实现动态代理,难免会对性能产生一些影响。
- 插件的定义需要明确需要拦截的对象、拦截的方法、拦截的方法参数。
- 插件将会改变MyBatis的底层设计,使用时务必谨慎。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。

